Trust, the cornerstone of any relationship, holds profound significance in our interconnected world. Whether it be interpersonal, inter-corporate, or even between governments, trust is the linchpin upon which successful relationships are built. Partisia Blockchain, in its essence, is a catalyst for redefining trust in the digital realm.
“The art of enabling trust within an inherently untrusting environment.”
But how does Partisia Blockchain achieve this monumental feat?
The importance of trust is a concept we can all readily grasp. Yet, the question arises – what facilitates trust among entities? A critical factor in this equation is privacy. Trust cannot manifest in a realm of complete anonymity. However, it also cannot thrive in a domain of absolute transparency. The sweet spot lies in a harmonious blend of both, where transparency and privacy coexist to cultivate trust.
Consider a simple scenario: applying for a credit card. A bank, to grant you this privilege, requires crucial information about you – your identity, income, contact details, and credit history. These details are essential for the bank to extend its trust in you. However, if you knew that these details would be made public, including your transaction history, your willingness to apply for that credit card would understandably wane.
Upon closer examination, it becomes clear that privacy is the very bedrock upon which trust is constructed.
In our credit card example, you enter a trusted environment where you bestow your trust upon the credit card company to safeguard your personal data. The company is, of course, bound by its business model to keep the sanctity of this trust. However, there is an underlying vulnerability here – data breaches, unauthorized sales, or inadvertent data exposure. These are potential avenues through which your trust can be shattered. In such cases, you are placing trust in the environment.
On the other hand, a trustless environment requires no implicit trust in any single entity but still manages to perform necessary functions seamlessly. Enter the decentralized blockchain, a prime example of an environment where trust in an entity is unnecessary. Here, blocks are formed, and information is inscribed on the ledger without a single entity having dominion over the system. The laws of physics exemplify another trustless environment – they exist without needing trust because the system is transparent, having been measured and documented, and accessible to all for independent confirmation.
Partisia Blockchain ingeniously fuses these concepts to tackle the trust predicament. It enables two entities to work together within a trusted framework, devoid of any single entity’s control. The synergy of multiparty computation (MPC) and blockchain technology underpins this innovation.
MPC, a revolutionary technology, permits the computation of confidential data. It functions as an encryption technology, allowing input values to remain hidden while still computing answers. It empowers us to calculate the sum of 2 and 3 without revealing the original values. Envisaged in the late 1970s and officially introduced in 1988, MPC boasts an illustrious history, with over a thousand research papers and 15 years of practical implementation.
In parallel, blockchain, the other keystone of Partisia Blockchain, has been redefined to its very core. Through our distinctive BYOC tokenomics principles and an infinitely scalable architecture, we make trust in a trustless environment a reality for all – not just for those building on our platform.
By converging these two technologies, Partisia Blockchain democratizes trust within a trustless domain. This manifests as a wealth of opportunities: companies collaborating without exposing their confidential data, creating equitable, private, and accurate voting systems, returning control of data to users, and enabling monetization of data. In the heart of Partisia Blockchain’s mission lies the potential to revolutionize business models and unveil novel value propositions.
In today’s context, the healthcare sector by itself contributes to around 30% of the global data volume, while the pharmaceutical industry significantly adds to this data generation. Handling and utilizing data from these sectors are also subject to some of the strictest regulations due to the nature of data that often includes personally identifiable information. GDPR, internal policies, and other regulatory frameworks pose tough challenges when data is collected or shared beyond isolated data silos for analytical purposes.
Public and private blockchains serve as effective tools for maintaining an immutable and transparent log of transactions, which can be relied upon and examined by various stakeholders such as public authorities. However, when it comes to the actual manipulation and processing data, both public permissionless blockchains and private blockchains are insufficient due to the lack of privacy features. This is where Partisia Blockchains’ distinctive and proprietary secure multiparty computation (MPC) technology emerges as exceptionally valuable
Our MPC technology empowers individuals and organizations to preserve privacy right from the input stage. This entails breaking down data into many encrypted secrets, which are then shared with specialized MPC network nodes. Critically, these nodes remain unaware of the specific content they store or compute on. Predetermined private and public smart contracts establish protocols for computations and determine access privileges to the outcomes, as authorized by permissions.
The potential applications for private computations within the healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors are virtually limitless. In this article, we will explore some of the extensively discussed scenarios.
Privacy technologies play a pivotal role in enhancing the security and confidentiality of private DNA sequencing. With the advancements of genetic analysis techniques, individuals are increasingly seeking to unlock insights from their genomic data, but the sensitive nature of genetic information demands robust measures to preserve privacy. MPC offers solutions by enabling private computations on encrypted genetic data without the need to expose the raw data. This allows for collaborative research, personalized medical insights, and genetic advancements while ensuring that individuals retain control over their sensitive genetic details.
By employing these technologies, private DNA sequencing initiatives can preserve privacy, encourage data sharing for scientific progress, and mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized access or breaches of genetic information.
Traditional data sharing approaches often raise concerns about privacy breaches and data ownership when it comes to the almost abundant amount of sensitive patient information and proprietary research data for healthcare and pharmaceuticals. MPC addresses these challenges by allowing multiple parties to jointly analyze and derive insights from their respective datasets without actually revealing the raw data to each other, but only share valuable outputs.
In the context of clinical research, pharmaceutical companies and healthcare institutions can collaboratively conduct analyses on aggregated datasets while keeping individual patient information and proprietary data secret. This facilitates cross-institutional research without the need to centrally consolidate data, eliminating the risks of data exposure and unauthorized access. Different pharmaceutical companies, each possessing valuable proprietary data, can engage in joint studies without revealing their confidential insights.
This collaborative approach unlocks opportunities for discovering broader trends, identifying potential drug interactions, and conducting large-scale analyses that draw from diverse datasets. By preserving privacy and ownership, MPC encourages cooperation among entities that might have otherwise hesitated due to privacy concerns. In essence, MPC bridges the gap between robust data-driven insights and the need for privacy, fostering a new era of collaborative clinical research across previously isolated data silos and organizations.
MPC offers robust primitives to revolutionize supply chain management within the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries. In these sectors, ensuring the integrity, transparency, and security of the supply chain is of all importance, as any inefficiencies or vulnerabilities can have serious consequences for patient safety and product quality.
MPC provides a solution by enabling various stakeholders, including manufacturers, distributors, regulatory bodies, and even healthcare providers, to collaboratively manage the supply chain without revealing sensitive proprietary information to one another. This is particularly valuable when dealing with complex global supply networks involving multiple parties, each with their own data and interests. Parties can jointly verify and validate critical supply chain information, such as the authenticity of raw materials, production processes, transportation routes, and inventory levels.
For example, pharmaceutical companies can verify the authenticity and quality of raw materials supplied by third-party vendors without sharing their precise formulation details. Regulatory agencies can conduct audits and ensure compliance across the supply chain while preserving the confidentiality of manufacturing processes. Healthcare providers can track the provenance of medical devices or drugs to enhance patient safety and prevent counterfeiting.
MPC-driven supply chain management ensures trust among stakeholders by providing a secure environment for collaboration. It prevents fraud, minimizes the risk of data breaches, and streamlines information sharing. By harnessing the power of MPC, the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries can establish a more efficient, transparent, and secure supply chain ecosystem that ultimately benefits patients, regulatory compliance, and business operations alike.
MPC presents a transformative way for streamlining the recruitment process in clinical trials while upholding patient privacy and data security. Clinical trial recruitment often entails the sharing of sensitive patient information across multiple stakeholders, including healthcare providers, research institutions, and pharmaceutical companies. MPC offers an innovative approach by allowing these entities to collaboratively identify eligible participants without revealing individual patient details.
Using MPC, each participant contributes encrypted data, maintaining the confidentiality of their personal information. The parties can collectively perform computations on this encrypted data to match potential participants with specific trial criteria, such as medical history, demographic characteristics, or genetic markers. This process ensures that no party gains access to the raw data of others, mitigating privacy concerns.
MPC technology not only accelerates the participant matching process but also encourages broader collaboration among stakeholders who might otherwise hesitate to share sensitive patient data. This approach streamlines the recruitment process, reduces administrative burden, and respects patients’ privacy rights. Ultimately, MPC revolutionizes clinical trial recruitment by combining efficiency and data security, fostering trust among stakeholders and contributing to the advancement of medical research.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Changing the data market business model from buying and selling of your data to buying and selling the “use” of your data.
Current advertising data market industry involves selling and buying of data. Regardless of the type of data the advertisers are looking for, it’s all about collecting the data from various means, categorizing it, perhaps pseudo anonymizing it and selling the data to advertisers. And data, as it turns out, is a very lucrative business. The global market size of the advertising market is estimated to be US$600–800 billion and the internet makes up about half of that size.
You probably have heard this statement before. If it is free, you are probably the product being sold. And this is a very common way for the data market players to create a “free” application that allows the collection of data that the market players will buy and sell. The more accurate the data, the more valuable. Google, Facebook, Twitter, Microsoft, etc all use similar business models. But there are other players in this market, some you may have heard of in the news (Cambridge Analytics for example) or smaller companies that trade your data under the covers. They will collect from various sources, reshuffle, and resell the data to others.
But as with any business model, there are challenges and the data market is not without its share of issues.
Partisia Blockchain’s privacy first blockchain with research lead secure multiparty computation (sMPC) can help solve these issues and also provide data market participants with alternate business models that can bridge the gap between consumer privacy concerns and better data overall.
This changes the data market business model from buying and selling of your data to buying and selling the use of your data. By shifting the paradigm to a services model, new potential revenue streams become available while being able to solve some of the difficult challenges facing the advertising industry.
Projects like Blockchain-Ads and Kin are already looking to take advantage of this new model and we are exited to see where this will lead in the future.
Connect with us at build@partisiablockchain.com to see how we can help you create new business models, solve challenges and provide new incentives for the users to use your system.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
In 2018, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) came into effect, causing a wave of changes to terms and conditions in your favorite applications across the globe. GDPR aims to increase people’s control and rights over their own personal information and heavily penalizes companies that infringe on these rights. Infringing on the rights of EU citizens laid out in GDPR could result in a fine of €20 million or 4% of the annual global turnover of an enterprise, so compliance is strongly incentivized. This new regulation is widely considered a major turning point in data protection and privacy rights, starting a policy diffusion of similar data protection laws across the globe. GDPR is law in every member country of the European Union and establishes a “single data market” within the EEA. Similar regulations have also been adopted in California, Chile, Japan, South Africa, Argentina, Turkey and Brazil, among others.
GDPR (as well as many of the similar regulations) involves multiple core tenets, among others setting out the principles for which personal data can be used and processed. Lawful purposes of the use of personal data and the digital rights that citizens have over their personal data. While there are many different compliance aspects of data protection regulations, such as GDPR, here are a few examples of how our technology could help your organization stay compliant:
GDPR requires organizations processing personal data to transform the data in such a way that it cannot be connected to the person it was collected from (pseudonymization). Partisia Blockchain could help an enterprise disassociate a person from their (encrypted) data, assuring such pseudonymization through the use of multiparty computation (MPC) technology. This pseudonymization can also be done in a way to allow for continuous collection of data from the same individual, if required for e.g. a longer-term study.
Furthermore, the concept of MPC also can also aid in maintaining an individual’s control over their data, as e.g. the concept of MPC secret sharing can allow for useful outputs being generated without compromising the underlying data (see Multiparty computation: The beacon of privacy solutions explained). MPC (especially combined with a blockchain) can also therefore increase the security of personal data, as the data and calculations are all run in a decentralized fashion by nodes that are all independent from each other. Partisia Blockchain’s nodes and their operators are all independent, run independent systems and have been vetted for cybersecurity by Partisia Blockchain experts.
Another right laid out by GDPR is the so-called right of access. This is the right of people to be able to see how their data is being processed and with whom it is being shared. The ledger kept on a blockchain could help an organization provide an immutable record to ensure this right. For the same reason, the blockchain could help organizations provide the record of processing activities required for GDPR-compliance under certain circumstances as well. As opposed to some other blockchains, Partisia Blockchain also allows for the possibility of private data to be removed from the record. Essentially meaning that data entered into the blockchain can be erased later on, allowing for compliance with GDPR’s right of erasure (the right for people to have their personal data removed from a database).
Lastly, the geographical location of servers used to process personal data could sometimes mean the difference between compliance and a criminal offense. Partisia Blockchain’s jurisdiction management v1.0 allows organizations’ developers to specify the geographic location of nodes to be used in calculating personal data. This could for example allow for private data from the EU to only be sent to EU-based nodes, ensuring that the integrity of the single data market and the data rights of EU-citizens are not breached.
Partisia Blockchain is committed to empowering others in solving real-world problems using our cutting-edge technology. Data rights and data privacy challenges are two of these problems.
Please contact us, if you have any questions about how our technology could enable data privacy or think we can help your organization in improving its data protection architecture.
Contact information: build@partisiablockchain.com
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
The point of this document is to provide the shortest (and most intuitive) possible introduction to each of the technologies mentioned in the title. I hope I succeed in this endeavor.
The technologies in this document all — with exception of differential privacy — deal with “secure” computation on data. At a very high level, this means they can be used to perform an arbitrary computation on one or more pieces of data, while keeping this data private.
Secure multiparty computation, which is what we do here at Partisia, is the term for a fairly broad class of protocols that enable two separate entities (called parties) to compute a function, while revealing nothing except the output.
An MPC protocol typically proceeds in three phases: First the inputters secret-share their private inputs. This step can be thought of as each user sending a special type of encryption of their inputs to the nodes doing the computation. The encryption ensures, for example, that at least two out of three nodes are required to recover the input, and thus, we get a security model that relies on non-collusion. It could also be the case that all three nodes must collude to recover the input — in this case, we have a full threshold model (since all servers must collude to break privacy).
The next step involves the nodes (the servers A, B, and C) performing the computation on the encryptions (i.e., secret-shares) received in the input step.
When the nodes finish the computation, they will hold a secret-sharing of the output. Each node’s share is returned to the users, so they can recover the actual output.
As might be inferred from the figures above, MPC works particularly well if the computation nodes are well-connected. Indeed, what makes MPC expensive to run is all the data that the nodes have to send between each other.
MPC have been actively studied in academia since the early 1980s and there are a lot of good resources available to learn more about it:
Fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) solves a very old problem: Can I have my data encrypted and compute on it too? FHE is a tool that allows us to not only store data encrypted on a server, but which allows the server to compute on it as well, without having to decrypt it at any point.
A user encrypts their private data and uploads it to a server. However, unlike a traditional E2EE (End-to-End-Encrypted) scenario, the server can actually perform a computation on the user’s private data — directly on ciphertext. The result can then be decrypted by the user using their private key.
FHE, unlike MPC, relies on clever cryptographic computation, rather than clever cryptographic protocols. On the one hand, this means FHE requires less data to be sent between the server and client compared to MPC. On the other hand, FHE requires a lot of computation to be done by the server.
Practically speaking, FHE is slower than MPC (unless we have an incredibly slow network, or incredibly powerful computers).
Practical FHE is a relatively new technology that only came about in 2009. However, since then it has received quite a bit of interest, especially from “bigger” players like Microsoft or IBM.
Partisia Blockchain supports FHE solutions.
While both MPC and FHE allow us to compute anything, zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) systems allow us to compute proofs. In short, ZKP allows us to compute functions where the output is either “true” or “false”.
ZKPs are incredibly popular in the blockchain space, mainly for their role in “rollups”. The particular type of ZKPs used for rollups are ZK-SNARKs, which are succinct proofs. In a nutshell, a succinct proof is a proof whose size is some fixed (small) constant, and where verification is fast. This makes smart particularly useful for blockchains since the proof and verification are both onchain.
That said, ZK rollups don’t actually use the zero-knowledge property — they only use the soundness and succinctness properties of the proof scheme.
Soundness simply means that it is very difficult to construct a proof that appears valid, but in actuality is not.
ZKPs, like FHE, takes place between a single user and a verifier. The user has a secret and they wish to convince the verifier about some fact concerning this secret, without revealing the secret. ZKPs don’t designate a particular verifier, so anyone can usually check that a proof is correct.
The final private computation technology I will talk about here is trusted execution environments. A trusted execution environment, or TEE, is basically just a piece of hardware that is trusted to do the right thing. If we trust this particular type of hardware, then private computing is clearly doable.
TEEs, being hardware, are tightly connected to some hardware vendor. Often when TEEs are mentioned, what is really meant is something like Intel’s SGX or ARM TrustZone. SGX is the TEE used by Secret Network, for example.
The security model of TEEs is fairly different compared to the other technologies I have written about so far, in that it is a lot more opaque. Vulnerabilities have been demonstrated in different iterations of different TEE products, especially SGX.
Differential privacy is radically different from the previous technologies. (In this discussion I will exclude ZKPs since it does not allow general computations.)
While MPC, TEE and FHE all provide means of computing something on private data, they do not really care about what that something is.
For example, it is possible (albeit pointless) to compute the identity function using both MPC, TEE and FHE.
This is because MPC, TEE and FHE allow us to compute anything. In particular, they allow us to perform computations that are not really private.
At this point, we may ask: Well, why would we perform such a silly computation on private data? For some computations, it might be easy to see that it is not private (in the sense that the original input can easily be inferred from the output). However, there are many computations that are seemingly private, but which can also leak the input if we are not careful. For example, it has been shown that it is possible to extract machine learning models, simply by querying a prediction API. In another example it was shown that it is possible to extract the data that a model was trained on.
These issues all arise because there are no restrictions on the computation that is performed. Differential privacy tries to fix this.
Differential privacy is used to provide a fairly intuitive guarantee. Suppose we are given two databases A and B. The only difference between these two databases, is that a particular entry R exists in A but not in B. Differential privacy now states that, no matter which type of query we make on the database, we will not be able to guess whether we are interacting with A or B.
Naturally, this means that some queries cannot be allowed. For example, it is not possible to obtain differential privacy if one can simply ask “Is record R in the database?”. Generally, differential privacy is obtained by adding noise, or synthetic data, to the database as well as restricting the type of queries that are allowed.
What makes differential privacy different from MPC, TEE and FHE, is that differential privacy makes guarantees about the output of a computation, whereas MPC, TEE and FHE makes guarantees about the process of arriving at that output. In summary:
This also means that differential privacy is not in direct “competition” with MPC, TEE or FHE, but rather complements them.
While each technology has its specific advantages and use cases, it is our feeling that Partisia Blockchain’s MPC, backed by 35 years of research and practical implementation does seem to provide the most overall coverage of all possible scenarios with very little drawback.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
A blockchain, at its very core, is a way for everyone to agree on what the current state of the world is, without having to rely on a trusted authority.
Of course, by “everyone” we don’t actually mean everyone, but instead everyone who believes in the security model. Likewise, by “the world” we also don’t actually mean the world, but rather, whatever is currently written on the blockchain’s ledger. Nevertheless, well-known blockchains such as bitcoin or ethereum both have market caps in the 100s of billions of USD, which tells us that the technology excites people.
Programmable blockchains, in particular, are exciting because their “world” is very rich. On a programmable blockchain, the “world” is basically the current memory of a computer, and so, simply by being clever about how we design the programs that run on this computer, we can use it to accomplish almost anything.
Let’s digress for a bit and classify programs into three categories:
— Those that take a public input and produce a public output
— Those that take a private input and produce a public output
— Those that take a private input and produce a private output
A programmable blockchain such Ethereum supports programs of the first kind: Everyone sees what goes into a smart contract on Ethereum, and everyone sees what comes out again. This is great for some applications (like agreeing on who bought a NFT), but clearly not sufficient for others (like performing an auction).
Several solutions have surfaced which attempt to support the remaining two types of computations. Let’s take a brief look at some of them:
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are, in a nutshell, a way for someone to convince (i.e., prove to) someone that they know or possess something, without revealing anything about that something. One situation where this shows up, is when someone wishes to prove to someone else that they control a certain amount of tokens.
ZKPs can therefore be used for private-public and private-private computation, to a limited degree. ZKPs can only compute, well, proofs. This in particular means that the computations are limited to a binary “yes” or “no” output. Moreover, ZKPs are inherently single-user oriented, so it is not possible to perform a computation that takes multiple private inputs.
Note that a program that takes a public input, but produces a private input does not make sense. If everyone can see the program and what goes into it, then everyone can obviously see the output as well.
Another private computation technique is fully homomorphic encryption, or FHE as it is called for short. At its very basic, FHE is a way of encrypting data such that it is possible to perform computations directly on the encryption.
This immediately tells us that FHE for sure supports private input private output type computations.
However, FHE, like ZKPs, are oriented towards a single user scenario. This means that, although FHE can perform any computation (which ZKPs cannot do), they cannot perform a computation that receives private inputs from multiple users.
In contrast to the two above technologies (as well as the next one), trusted execution environments (shortened as TEEs) are a purely hardware based solution to the private computing problem we’re looking at.
A TEE is simply a piece of hardware that have been hardened in certain ways that make it hard to break into. If we believe this to be the case, then a TEE can be used to perform the private input, public/private output computations we’re interested in.
Inputs are encrypted using a key stored only on the TEE, and computations take place on the TEE after decryption. When the computation is done, the output is encrypted (or not, depending on whether the output should be public or private) and then output by the TEE. In this way.
TEEs therefore clearly support the type of single-private-input computations talked about so far. However, the situation is a bit complicated if we want to receive inputs from multiple sources. Indeed, the only way that can be possible, is to make sure the same key is stored on everyone’s TEE.
The last tech I will look at is secure multiparty computation, or MPC. This privacy tech supports both types of computations, just like FHE and ZKPs, but where it distinguishes itself is that it naturally supports private inputs from multiple sources. Indeed, there’s a reason it’s called secure multiparty computation.
This makes MPC especially suited for a blockchain because of its multi-user nature.
The above categorization leaves out a lot of details, since it talked about neither the security models that each of the technologies use, nor about their efficiency.
Each of the four technologies above operate in a particular security model, and none of the models are exactly the same. Likewise, they each have some properties that make them desirable compared to the others. (For example, FHE requires more computation, but less communication, than MPC.)
In general, MPC does seem to come out on top, and is the only technology that easily supports computations where multiple users provide inputs. MPC, by its nature, is a decentralized technology, which is probably why it works so well in a blockchain setting. That being said, an ideal world would probably use all of the technologies in a carefully created orchestration to ensure the best guarantees in terms of both security and efficiency.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
At present, it requires a fair amount of technology knowledge to build and support a node in PBC. While many who do not have a technology background have been able to build and maintain nodes, it still creates a barrier that many individuals or organizations feel hesitant to cross. The other challenge is the current staking and job association process. Because the staked MPC tokens in a node are being used as collateral for all the types of jobs the node is running, unstaking and unassociating tokens that are being used can be a challenge.
This is why we are putting focus on implementing a simpler node setup and operations process. This will allow easier setup of nodes as well as easier associating and dissociating of your tokens.
These new features will be rolled out in phases, with the first one being automatic node registration. A simplified registration process will be rolled out where just the configs on your node will kickstart the KYC/KYB and the registration process.
Second phase of the project will be to simplify the association and dissociation of your staked tokens. It will all be a part of our “Staking 2.0” model, which will look to make it easier and less restrictive for both node operators and delegated stakers to manage their stakes.
Running a node will still require some level of technical skill. We hope by automating some of the process, it will make it less confusing and easier for the registration process.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
As we continue to see development occurring on our blockchain, we are always on the lookout for feedback on how to improve our platform, either to make it easier for developers to develop on, or to add new functionalities to help improve the product offering by the teams developing on our chain.
In the last 6 months we’ve been listening to the developers and have been working on various new functionalities and features that should help improve the quality and functionality of the projects. Some of them came in the form of development tools which we reviewed last week.
In this article, we will review the new feature sets that are upcoming to help developers improve upon the existing features or add new functionalities.
Some of these features will also create new use cases for the MPC tokens
Improvements in the PBC as a Second Layer Functionality
One of our main value propositions is our cross-chain bridge (Hermes). This unique bridge and gas payment system allows other chains to be a usable asset in Partisia Blockchain. It is this bridge that allows other chains to call our MPC technology as a service and pay for it using their native coins. But at the moment the data that is transferred is through manual data attestation, and the transfer only occurs in one way (PBC -> EVM).
By implementing BYOC messages to be supportable, we will now implement a two way communication system. This allows for the smart contract writer to hook events that are happening in the EVM back to PBC. Through adding a MPC powered threshold key and tying our oracle servers to collateralize these data through MPC tokens, developers will now be able to create an automated bidirectional flow of data between the EVM and PBC. This opens up additional functionality, such as adding message information in NFTs and allowing them to be transferable cross chain, or sending and receiving of data during the actual bridging transfers.
Staking as an Insurance
Currently, once the funds inside a smart contract runs out, the contract gets deleted. We will be creating a new method to allow for SC owners to stake their MPC tokens as insurance to allow for these smart contracts to continue to live on even if the funds run out of the contract. This will allow for both a safety mechanism in the event funds do run out and also introduce another use for MPC tokens.
ZK Contract Lifetime Beyond 28 Days
Currently the data in a ZK contract lasts for 28 days. Going forward, we will introduce a way to allow for this data to be extendable to go past the 28 days through staking MPC tokens and re-funding the smart contract.
ZK Computation in Batches
This feature will allow for multiple ZK computations to be batchable so that you do not have to execute each and every computation one at a time.
Allow ZK Contracts to Control User Data
Currently the developers writing ZK smart contracts do not have flexible control of the Zero Knowledge data. Through this feature, we will allow for developers to have greater control of the type of data and the control of how the data will be used.
We hope that the above will both help improve the speed in which development can be done as well as allow for new features to be implementable by the developers.
As each of the items complete, we will make a separate announcement in our development channels.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Bitcoin is what started it all. The coin that began the blockchain industry and even over 14 years after its initial creation, and after so many new coins trying to improve upon the original, it still stands as the king of crypto currency. It is still the main form used as payment in the blockchain industry and others are either built as bringing functionality more than being a currency or is relegated as 2nd place at best.
As mentioned in our interoperability article, the current blockchain L1 ecosystem are basically in a zero sum game. Every chain is trying to be faster, cheaper, more secure and easier to build on. And each blockchain operates by using their own native coin for their transaction fees. And as DeFi came into the picture, DEX’s began looking for options to allow for swapping between chains that were not native to itself. Enter wrapped tokens.
Currently in the DeFi ecosystem, there is only one way to trade BTC. By creating a wrapped version of itself. Whether its wBTC, HBTC or renBTC, etc, it is basically all a similar form of custodying a BTC and minting an IOU type mirror token on the native network. When the smart contract holding the mirror coin is burned, then the locked, or custodied real bitcoin is released. One of the problem in this system is that you must give trust to the custodians. Not only does this go against the trustless-system ethos of public blockchains, if something happens to the custodians (hack, out of business, etc) then your wrapped tokens could be lost or become worthless.
While Partisia Blockchain can implement wrapped bitcoin as BYOC asset easily, this fundamental architecture of wrapped bitcoin tied to a custody goes against the principles of allowing native coins to be used as a form of transaction payment in the blockchain. As mentioned above, from price parity between real and wrapped BTC, to security issues raised by using a custodian (corruption or even worse, a hack in the custody system) there were too many compromises. And so we are taking the road less traveled and working toward finding a solution to allow for native bitcoin to be usable as an asset in the Partisia Blockchain.
This means we are creating a multi-phase program to build this road. The first phase will be a research phase. We’ve already begun this effort and hope to complete it in the next few months. Once the research is complete, we will know the effort needed and then will engage in an architecture and engineering sessions to plan out the work to accomplish this.
This has some major possible benefits. From allowing users to spend native BTC as gas transactions for applications built on the Partisia Blockchain, to creating a native token swap between BTC and another BYOC chain, or even helping to scale transactions in the bitcoin network, implementing native BTC directly in the Partisia Blockchain network will open up new possibilities in the blockchain industry as a whole.
Please be on the lookout for future news of the results of this research.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Currently our MPC protocol (called REAL) computes binary protocols, but we are going to add an arithmetic protocol in the not too distant future. The “binary” or “arithmetic” property of a protocol is not an indication of what is possible, but rather what is efficient.
Every MPC protocol operates on units of some type, and all applications using MPC are built using a very very small set of operations on this type. Some types are better at some applications than others, which motivates supporting protocols that operate on different unit types.
In binary REAL, the “unit type” is a bit; that is, a number that is either 0 or 1. The only operations we can perform on these bits are exclusive or and conjunction (or XOR and AND). All other protocols have to be built using one or more bits, and a combination of XOR and AND operations.
This naturally means that protocols that can be efficiently expressed as a combination of XOR and AND operations, would be efficient in binary REAL. Such operations include comparisons, any kind of bit manipulation, rotations, shifts, and so on.
On the other hand, operations that require a lot of XOR and AND operations, would be in-efficient. For example, additions, subtractions, multiplications and essentially any operation that is “arithmetic” in nature.
In Arithmetic REAL, on the other hand, the “unit type” is a number between 0 and n (for some n) — and the only operations we can perform are addition and multiplication.
Arithmetic REAL therefore performs very well in applications with a lot of arithmetic. That is, a lot of additions, subtractions, multiplications and so on. On the other hand, applications with a lot of non-arithmetic operations are expensive. For example, it is not very easy to compare two numbers, if all you’re allowed to do is add and multiply the two numbers being compared with each other.
Binary REAL, being binary (or boolean) in nature, performs well on applications that are, well, binary in nature. This includes applications such as
Arithmetic REAL, being arithmetic, performs well on arithmetic applications:
By enabling arithmetic computations in Partisia Blockchain, we aim to open up new solutions as well as allow for cheaper and easier implementation of existing ones. From health record analysis to private voting in a massive scale, we hope to achieve a much wider acceptance of MPC as a perfect solution to enabling computation while protecting individual users’ privacy.
Be on the lookout for this sometime in the 3rd or 4th quarter of 2023.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Guest Blog by Oleg Ivanov, Co-Founder of Weezi/Secondlane.
SecondLane is co-founded by top players in the Web3 OTC market, combining advanced tech, licensing and historical business volume in the secondary market.
With SecondLane project teams, advisors and investors can now:
Or
The technology stack has been built over the past two years with Weezi team, who now migrated full-time to SecondLane.
There are six essential features that are gradually being automated and released by the team. Each of these features represents the steps of a typical OTC deal.
Such features are bundled into three versions of the SecondLane platform, with SecondLane V1 up and running on EVM-compatible chains.
We are honored to be trusted by Partisia Blockchain to integrate the Partisia ecosystem’s main characteristics into our SecondLane V2 release.
The core element of SecondLane V2 is automated on-chain onboarding and verification of users and assets. This has to be done in (a) a compliant, and (b) privacy-preserving form; so that buyers and sellers are sure that their information is not known to the public.
Partisia Blockchain’s ZK MPC technology, coupled with the decentralized consensus of oracles, is the right mix of tools for our task.
The innovations set to be introduced by Partisia Blockchain is long awaited in the market, and we at SecondLane are excited to be among the first partners to integrate those into our product for our client base.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
One of the main priorities for any blockchain is adoption. The stronger the base that are developing on the chain, the stronger the chain. And one of the important factors for adoption is the ease of development on a chain. For that purpose, we have been working hard on tools to help developers develop and deploy on our chain.
The below are some of the key frameworks, contracts and libraries that will help developers create amazing applications on our chain which we are planning to release in the next 6 months.
With these tools, we hope we will allow development in our chain to be easier, and we will continue to focus on building new tools to help the development community.
Many of these items will launch as they get completed, with a full completion date of around the end of 4th Quarter.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
One of Partisia Blockchain’s core values is in collaboration. Our belief is that one of the main paths to advancing the further adoption of the blockchain industry is through working together. And this belief is built into our blockchain architecture.
As mentioned in our interoperability article, the current blockchain ecosystem is kind of like going to an amusement park. You can play in an ecosystem but only if you pay using their native token.
Partisia Blockchain’s payment mechanism broke away from this paradigm and designed a tokenomics that uses other chains tokens. We started off with Ethereum, then added Polygon USDC, and then integrated BNB into the chain. Now, we are bringing the ability to onboarding tokens to the community.
With the new Ethereum BYOC Framework, we are enabling the ability for any community developer to submit a proposal to onboard a ERC20 or a BEP20 token of their choice that is running on the respective chains into the Partisia Blockchain bridge. This brings the control of adding a token into the Partisia Blockchain to the public.
How it works:
By enabling this important roadmap item, we bring the control of onboarding any new Eth or BNB based asset into our unique bridge to not only be used as a swappable tokens, but allow it to be usable as gas for transacting in the Partisia Blockchain network. Whether you are a dApp that wants to add privacy services into your existing application, or create a unique DeFi solution on Partisia Blockchain that allows for swift easy swaps between assets while preventing front running and sandwich attacks through MPC, all of the value proposition that Partisia Blockchain offers is now available to any system running in the Etherium, Polygon or BNB chains.
Please look out for this feature being launched sometime in the 3rd/4th quarter.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Scalability has been something that architects have been grappling with for many years. In the technology space, being able to scale both vertically (adding capacity) and horizontally (adding instances) has been grappled with in all parts of the technology stack. Do you add more transistors in a CPU or add cores to work together? Do you add more space in a hard drive or add multiple hard drives to work together? Do you build a faster computer, or create a software architecture to use multiple computers in sync?
One thing is for certain however. Scaling vertically has limits. There is only so much CPU, memory, storage you can add to a single system before it runs out of capacity.
Blockchain space is no exception. As adoption grows, so must the ability for a blockchain to handle the additional transaction on chain as a result. And in the blockchain space, we call it TPS (transactions per second) This is a combination of two metrics;
Different blockchains use different architectures to try and achieve faster throughput. For finalization, there are things like probabilistic and deterministic finalization. To achieve a higher number of transactions, blockchains have turned to sharding, and added on different rollup technologies like ZK or optimistic roll ups.
To create the fastest blockchain, you have to first look at what can theoretically be achieved for the above two factors. For the finalization time, the fastest is instant. As soon as the block is created, you want it to be finalized as fast as possible. For the number of transactions in a block, you want to be able to put the number of transactions in a blockchain can handle to be as much as possible. The more transactions you can process at the same time, the faster your chain will be. And all of this needs to be done in a secure manner. So how does Partisia Blockchain handle these two challenges?
For finalization, PBC has implemented a unique consensus model that consists of three parts.
This unique finalization model allows for blocks to be created and finalized in real time with the only limit being the time it takes for the verification signatures to propagate throughout the network. (More info in PBC’s yellow paper section 3.1)
While the term “sharding” has been popularized by blockchain, its actually a term that was coined back in the 1990s, by an online video game company, of all places. During the initial popularization of MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role-playing games) the company building the game Ultima Online ran into a scalability problem. To solve the problem of scaling out huge worlds for hundreds of thousands of users to interact with, they came up with a database scaling architecture and coined it “Sharding” This sharding architecture caught on and is now actively being used by many different database products, including MySQL, Oracle DB and MSSQL.
Blockchain has borrowed the term but if you look at the general architecture of most blockchains, it does not conform to the general principles of what sharding really means. In blockchain sharding, while blocks may get created in parallel, it still gets appended to the end of a single chain.
Through “speed of light” finalization we tackled the issue of creating finalization instantly. For the transaction per block issue, we looked to architect the sharding model according to the definition of what sharding really is; True parallel processing of data.
Just like how it is in traditional databases, in Partisia Blockchain, each shard is an independent blockchain. And each shard ,or blockchain, is capable of independently creating, validating and confirming a block. This architecture goes back to the original definition of what a shard is and allows for true parallel processing of blocks. And in the event congestion is detected, the system automatically creates a new shard adding additional capacity dynamically. Through this dynamic scalability architecture, Partisia Blockchain can theoretically scale infinitely, only limited by the number of nodes in the blockchain.
By creating a programming language that allows for developers to use MPC in a generic way, Partisia Blockchain Foundation has made the creation of applications that can harness the power of MPC for different use cases a possibility. Partisia has been at the forefront of providing private MPC solutions since 2008. And by layering this technology on top of an interoperable and scalable blockchain, Partisia Blockchain is paving the way for anyone to create blockchain solutions that can balance privacy and transparency to build trust and ensure integrity.
To learn more about different use cases or partner with us for solutions, please visit partisiablockchain.com, check out our Medium articles, development documentations or email us at build@partisiablockchain.com.
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Have you ever taken a trip to an amusement park? Then you are probably familiar with “amusement park dollars”. The park encouraging you to exchange your native currency to “amusement park” dollars because the only thing that is accepted in that amusement park is the currency of the amusement park. And of course, those amusement park dollars are not good anywhere else except in that park.
This is similar to how the public blockchain industry’s tokenomics works. If you want to play in the Solana ecosystem, you have to have the SOL token. Same with Cardano, where you need to pay using ADA. Theta is TFUEL, etc. The entire ecosystem model revolves around their specific currency.
And like amusement parks, every blockchain is in competition with each other. “We’re cheaper. We’re faster. We’re the easiest to develop on.” So on and so on…
In fact this “competition with each other” scenario has been seen throughout history. And it’s quite interesting to see, historically, who has been the winners in these types of competitions. VHS vs Beta in the 70’s, The desktop wars in the 80s, Ethernet vs Token Ring in the 90’s, search engine wars in the 2000’s, and the streaming war that is currently ongoing. And in almost all cases, the winners in these “wars” was the one who was collaborating rather than competing with others.
So the big question is….. Who is going to win the L1 public blockchain wars?
As mentioned above, the current state of the public “blockchain wars” is all about competing with everyone. The combination of every chain saying they are faster and cheaper, with the silo’ed tokenomic model of each chain forcing users to spend only in their currency locks every dApp in their own ecosystem. This is why interoperability has become one of the biggest topics in the industry.
But can we do it differently?
One of Partisia Blockchains core principles is interoperability. This is because our vision is to enable anyone to create solutions that help establish trust and foster collaboration and this means having an architecture that supports interoperability.
So in this regard Partisia Blockchain created a platform from scratch. And following the vision and principles we are adhering to, we created the concept of Bring Your Own Coin (BYOC).
BYOC basically means the users of the chain can pay for using apps developed on PBC using the coin they are most comfortable with. Or in other words, the gas payment on our chain is other liquid coins. This allows for the following possible features.
The Hermes bridge is a double-entry bookkeeping system securing the bridged asset through our MPC multi-sig oracle key. Currently supporting Ethereum, BNB and Polygon USDC, our roadmap includes others like bitcoin, ADA, XTZ and allows for simple integration to all other EVM compatible tokens. This interoperability and gas payment model opens up a variety of interesting use cases, such as the ability for users to interact with any dApp using their own currency of choice.
Our MPC-as-a-Service is also a unique feature of Partisia Blockchain. Our core vision is empowering anyone to be able to utilize our MPC services and to achieve this vision, we designed an architecture that allows anyone to call the blockchain, regardless of where their core app is built. Whether it is a traditional Web2 or a Web3 application that is built on a different chain, both can call Partisia Blockchain and compute using secret inputs without needing to port their entire application stack over to Partisia Blockchain.

By creating a programming language that allows for developers to use MPC in a generic way, and combining it with a unique interoperability and a scalability architecture, Partisia Blockchain Foundation has made the creation of applications that can harness the power of MPC for different use cases a possibility. Partisia has been at the forefront of providing private MPC solutions since 2008. And by layering this technology on top of an interoperable and scalable blockchain, Partisia Blockchain is now paving the way for anyone to create solutions that can balance privacy and transparency to build trust.
To learn more about different use cases or partner with us for solutions, please visit partisiablockchain.com, check out our Medium articles, development documentations or email us at build@partisiablockchain.com.
Guest blog by Vilma Catani and Radu Pavel, Co-founders of Monadi.
Monadi is a platform for managing sustainability data and reporting in compliance with the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). This EU-imposed regulation mandates companies to disclose information regarding their Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) impacts. With the CSRD set to come into effect in 2024, approximately 50,000 companies in the European Union will be obligated to report their ESG data. Monadi aims to simplify and streamline this process while also leveraging the business opportunities it presents.
Sustainability reporting requires management of a vast amount of data, which is a complex task. Firstly, sustainability data is often scattered throughout various departments and external sources within an organisation. Monadi aims to consolidate all of this data into a unified platform. Secondly, the timeline for achieving sustainability goals can extend for several decades, even as far as 2050. We want to be the go-to solution for managing both short-term and long-term sustainability goals.
Monadi has chosen Partisia Blockchain to help ensure safe, credible, and transparent management of data, enabling comparable results across organisations. Leveraging systems like Multi Party Computing and Zero-Knowledge proofs, Partisia Blockchain offers solutions for data transparency, credibility, and encryption. Given the sensitivity of sustainability data, many companies are reluctant to share it. However, the highly secure solutions offered by Partisia Blockchain provide a game-changing approach for ensuring data protection and privacy.
The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is expected to be released by the end of this summer, offering the public access to the first use case: “Male-female pay gap” which adheres to the European Sustainability Reporting Standards and utilises Partisia’s Multi Party Computing (MPC) capabilities to privately collect and calculate the pay gap data between genders within the organisations, which is then added on-chain. The platform also provides dashboards and other features to monitor progress and generate reports ready for CSRD reporting.
In summary, Monadi is an innovative platform for management and reporting of sustainability data for companies operating under the CSRD. By leveraging Partisia Blockchain’s technologies and ensuring data privacy, Monadi offers a solution that simplifies compliance and empowers organisations to progress towards their sustainability goals.
— — — —
Website and social channels coming soon…
Guest blog by Dhruv Malik, Sr Smart Contract Engineer and Gael Bokongo CEO and Co-founder at Muwpay.
Muwpay, founded by an educated and innovation-driven team, is on a mission to dissolve the barriers of cross-chain universes by designing a flexible, interoperable user experience. The team has been developing their pioneering protocol called MUWP (Multi Underlying Wrapped Payment), a multi-token protocol adaptable to a variety of formats such as smart wallets, smart widgets, or SDK.
We are privileged to be trusted by Partisia Blockchain, one of the key players in the blockchain space known for secure and private computation services. This partnership has led to the creation of a smart wallet specific to the Partisia community. Thanks to the technical support and global vision of the Partisia Blockchain Foundation, a secure environment has been established where users can experience cutting-edge solutions. This collaborative approach holds vast potential for the future.
We were thrilled to be interviewed by the Partisia Blockchain team to explain our journey so far on our first partnership with such a significant figure in the blockchain industry. Check it out here.
Muwpay is developing the smart wallet and cross-DEXliquidity aggregator protocol with the aim of:
Thus, we provide full end-to-end wallet as a service for Partisia ecosystem
This will be the cross-native wallet that works as follows:
And then see the benefits of paying instantaneously in stablecoins using multiple denominations and low slippage.
For us, Partisia Blockchain ecosystem’s main characteristics were critical to launching our project on this ecosystem, services such as:
MUWP offers extensive benefits for crypto holders. It streamlines the conversion of tokens, reduces operational risks through secure and private computation services, and decreases gas fees by enabling any token for payment. The shards feature also improves transaction throughput. As such, MUWP enhances the overall cryptocurrency user experience, taking it a notch higher.
Thus, we have been progressing to build the smart contract protocol layer and also the mobile wallet, and are poised to release the beta test version around July. Feel free to follow the website muwpay.com for more information.
Overall, the partnership between Muwpay and Partisia Blockchain, and the innovations they are set to introduce, demonstrates a clear vision for a more efficient, secure, and user-friendly future in the world of blockchain technology.
Guest blog from Moojan Asghari, Thousand Faces Co-founder and CEO
Thousand Faces is a reward-based crowdfunding platform powered by Partisia Blockchain. It aims to address funding gaps and support impact-driven female founders. With only 1.9% of venture capital funding allocated to all-female founding teams, there is a huge gender gap in funding.
While women currently make just 30% of climate-related decisions, they have proven to excel in building sustainable businesses, resulting in organizations led by women being 2.5 times more profitable. Recognizing the significance of funding more women and providing them with leadership opportunities, Thousand Faces seeks to democratize funding for women and minorities by offering both financial resources and a powerful network.
Driven by the frustration of limited funding and support for underrepresented groups, we embarked on a mission to leverage the principles of Web3, namely transparency, ownership, and decentralization, to serve both people and the planet. The lack of inclusivity in investment decisions, particularly regarding women and minority-led ventures, poses a significant challenge. Research shows that unconscious bias often leads investors to favor individuals who resemble themselves, perpetuating the underfunding of women and minorities. To address this issue, Thousand Faces turned to the powerful capabilities of Partisia Blockchain.
Partisia Blockchain introduces an innovative approach to tackle this problem through its zero-knowledge and voting mechanisms. Leveraging the secure content and zero-knowledge voting developed by Partisia Blockchain, Thousand Faces is building a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). This empowers the creation of an inclusive and transparent voting system that ensures the active participation of a diverse community.
The voting system operates at two levels. Firstly, a diverse jury panel plays a crucial role in the initial voting stage, utilizing the zero-knowledge bootstrapping of Partisia Blockchain to ensure process security. Additionally, a committee-based second level of voting includes the entire community, consisting of token holders and NFT members. This approach guarantees that community members, who act as funders and supporters, have a voice in selecting projects and monitoring their progress.
Thousand Faces has already launched its first membership and NFT collection, available on the website for interested individuals to explore and apply for private sales. You can apply to join the Thousand Faces membership on the allowlist here. The platform has also established a dedicated member’s board and successfully completed its inaugural acceleration program for female founders. We received over 200 applications from nearly 80 countries, aligning with diverse UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). From Kenya, Nigeria, Germany, Lebanon, Singapore, and the UK, six outstanding projects reached the final round. At the awards ceremony in April, the top three were granted US$30,000, with support from sponsors including Sandbox and the World of Women Foundation.
To stay updated on our latest developments and join us on our exciting journey, follow us on Twitter or visit our website. We’re excited to be part of the Partisia Blockchain ecosystem and are fully committed to transforming the inclusivity in the web3 space and beyond.
Website | Twitter | Linkedin | Telegram | Discord | Medium | Instagram
Guest blog from Mariia Kren, eTrusty Co-founder and CEO
Corruption represents a significant hindrance to both economic growth and human development. Among various processes, procurement is particularly susceptible to corrupt practices, leading to substantial financial losses estimated at around €400 billion per year in European public procurement.
Furthermore, the procurement market faces another challenge as it is expected to grow from US$12–US$13 trillion in the next five years to approximately US$16–US$19 trillion. As procurement costs rise, the need for tender sites to scale rapidly becomes increasingly important.
In our commitment to combat corruption, restore trust in procurement, and facilitate the scalability of procurement platforms, we are delighted to introduce eTrusty.
By implementing blockchain technology, eTrusty fosters transparency through a publicly accessible ledger, ensuring secure and transparent monitoring of transactions and information. Moreover, it provides a decentralized and immutable data state, ensuring the secure storage of data. These features effectively mitigate client distrust and significantly reduce the risks associated with technical fraud.
A pivotal aspect of our confidence in implementing eTrusty lies in our collaboration with Partisia Blockchain. By harnessing the power of Multiparty Computation (MPC) with Zero-Knowledge (ZK), eTrusty establishes customizable layers of privacy for various aspects of procurement, such as applicants, judges, and results. This robust privacy framework effectively combats human fraud, coercive practices, and bribery. To elevate the scalability of eTrusty, we have integrated Partisia’s groundbreaking solution, Bring Your Own Coin, to establish a cross-border solution. Furthermore, the architecture of eTrusty enables customization to cater to diverse procurement requirements.
Currently, we are diligently developing our smart contracts, user interface, and back-end prototype. Our Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is scheduled to be completed in the last quarter of 2023. This MVP will be a web application showcasing all the key features of our API, which we plan to seamlessly integrate into existing tender platforms in the future.
The mission undertaken by eTrusty is of utmost importance and highly relevant in the current business landscape, where accountability and transparency are increasingly demanded. We eagerly anticipate the continued evolution of eTrusty’s protocol and its meaningful contribution to the broader objective of cultivating a fairer and more sustainable global economy.
As proud members of the Partisia Blockchain ecosystem, we invite you to follow us on our journey to shape the future of procurement!
15 May 2023 — Today marks the launch of the Insights Network’s Parti.com, a unique platform that empowers creators with Web3 technology and cryptocurrency transactions for content monetization. This hub for creators provides unprecedented control over their creative output, while enabling them to earn revenue through self-hosted cryptocurrency. Parti.com is built on the open-source technology of Partisia Blockchain, renowned as the world’s first privacy-preserving, next-generation blockchain. It offers multi-network currency support and affordable transactions.
Parti.com, designed to be an inclusive platform, provides users with self-custody of their funds, ensuring complete ownership and control. The platform’s ease of use, facilitated by a straightforward account setup process via Discord or Twitter login, makes it accessible to both creators and consumers.
Parti.com simplifies the buying and selling process by completely removing third parties, such as traditional banks and other Web2 financial institutions, from the monetization process. This marks the first time that creators and content consumers can interact within a completely peer-to-peer network, without payment processors or middlemen holding user funds.
One of the key features of Parti.com is the ability to create and sell NFTs directly from creator profiles, simplifying the process of content monetization. The AI Zone helps new creators generate art rapidly; thereby, democratizing the digital art landscape.
Furthermore, Parti.com breaks new ground with its application of NFTs as utility tokens, granting access to exclusive content. This concept, known as “tokengating”, is set to change the way creators engage with their audiences, fostering deep, meaningful connections. An easy-to-understand use case could involve a content creator creating a pass with a maximum of 1,000 units sold. All holders of this NFT, upon signing into their platform with their wallet, are granted access to all of the creator’s private content available on their Parti.com channel. This process, completely automated by the blockchain, creates a direct, creator-to-user connection that surpasses anything the current market offers, be it Web2 or Web3. The platform also accommodates transactions with ETH in Metamask, providing users with the flexibility to transact in their preferred cryptocurrency.
To jumpstart the network, Parti.com offers the unique “Hall of Fame” (HOF) NFT pass. This limited NFT access pass grants users master access to the entire network, enabling the first users to buy into the entire network and never have to pay for content access again. Coupled with the platform’s low transaction fees, this feature is set to redefine the value proposition for content creators and consumers. In the future, if users wish to leave the network, they can always offer the pass for sale in the upcoming NFT marketplace.
Parti tokens function as the platform’s currency, which users can use for buying and selling. Creators incur a 0.1% platform fee when selling NFTs or content in Parti tokens, compared to a 5% fee when using ETH or USDC. Although this fee model is subject to change, there is currently no fee for creators for at least the next three months, serving as an incentive to join the network early.
In essence, Parti.com is more than just a platform — it is a revolution in the creator economy. It is dedicated to providing creators with the tools they need to thrive, while offering consumers a new way to interact with and support their favorite creators. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, Parti.com stands at the forefront, poised to transform the creator economy with the power of Web3.
About Parti.com: Parti.com is built by Insights Network, a web3 Company founded in 2017 and through multiple market cycles.
About Partisia Blockchain Foundation: Partisia Blockchain Foundation brings unparalleled opportunities by empowering privacy-preserving, interoperable and sustainable innovation for fairness and transparency. It fuels the most secure and efficient networks to solve global problems. Distilled with more than 30 years of rigorous research, Partisia™ Blockchain future-proofs solutions, solves tomorrow’s challenges by powering fair, secure, distribution of benefits. While preserving privacy and confidentiality, it brings accountable, transparent and decentralized governance. Learn more: www.PartisiaBlockchain.com
Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Guest blog from Vlad Chejkov, Blockchain-Ads Founder
As the founder of Blockchain-Ads, I am thrilled to be featured in the Ecosystem Spotlight, where we are shedding light on the revolutionary changes we are bringing to the Web3 industry.
Blockchain-Ads is specifically designed to bridge a gap in the market where Web3 brands struggle to reach their ideal customers. Traditional ad networks often restrict crypto-related promotions, and none of the crypto ad networks currently allow targeting based on users’ on-chain behaviour.
Blockchain-Ads platform offers Web3 brands the opportunity to connect with their target audiences efficiently and effectively, outperforming the competitors 10 to 1.
Our collaboration with Partisia Blockchain has been fundamental to our success. Their pioneering multiparty computation (MPC) and zero-knowledge (ZK) technologies serve as the backbone of our solution. They ensure user data is processed securely while facilitating targeted advertising. This approach respects user privacy and transforms the digital advertising landscape without revealing any underlying data or compromising user privacy.
Currently, we are at an exciting juncture. We are preparing to launch Partisia smart contracts on testnet in the first half of May. It is a crucial step that will help us refine our solution in a secure environment before launching on the mainnet.
As we forge ahead, our mission is clear: to disrupt the conventional, centralized advertising industry with a decentralized, privacy-preserving, and cost-effective solution. We aim to redefine privacy and user control in the digital advertising landscape, tailoring specifically to the needs of Web3 brands.
For more insights into our progress and to stay abreast of our exciting journey, follow us on Twitter or reach out through our website. We are proud to be part of the innovative Partisia Blockchain ecosystem and look forward to reshaping the future of privacy-preserving advertising in the Web3 space.
Guest blog from Gordon Povey CEO & Founder at Kin
Kin is a Web3 ad-free search engine built around community, transparency, and privacy. The prototype has been operational for over a year and on 1 May 2023 we launched the Kin beta https://searchkin.com.
Our aim is to be a disruptor and so we are highly differentiated from incumbent search engines like Google.
We are building a community of users that believe in Web3 principles. We use blockchain and a smart contract for transparency. We will use multiparty computation (MPC) technology to ensure maximum privacy for users at all times.
We have thrown out the traditional advertising business model where the user is the product to be sold to advertisers. Instead, we become a broker of both information and also online products.
So metaphorically, if you want to go to the library for information, we become your personal librarian and try to find exactly what you are looking for without trying to sell you anything or distract you along the way. Then, if you do want to go to the shopping mall (metaphorically) to buy something, we are like your personal shopper trying to find exactly what you want and can even uncover local or artisan products that are usually difficult to find online.
We generate revenue as a broker only when we find what you really want. By taking this approach, we find information that is less skewed by large commercial SEO budgets, and we can discover online products that are often hidden by advertising and brand dominance.
We knew we needed to work with a Layer 1 blockchain so that we could mint our own tokens. We also knew that we needed a secure way to process user data while maintaining complete privacy. The fact that Partisia Blockchain was offering not just a blockchain, but also MPC capabilities made it a front runner.
We have just launched the Kin beta. The organic search (for web, news, images and videos) is working extremely well. We believe it provides better results than the incumbent search engines (try it for yourself and compare our results to other search engines).
We still have work to do on the shopping searches, which are limited and UK-centric at present. We will also be turning on the user rewards system very soon. To fund future developments, we are opening another token pre-sale, which will allow early supporters of our project to buy tokens at a discounted price. The funds will be used for the product launch and marketing, and for ongoing developments such as the implementation of our community-based training (using xAI methods) which is included in a patent we recently had granted.
Learn more about us: Search engine, Website, Email, Telegram, Twitter, LinkedIn
Most may not know, but generating random numbers is hard. It is quite surprising because many people will think, “well, I can just come up with a random number off the top of my head!” However, randomly coming up with a number in your head, as well as other solutions to generate random numbers has fundamental flaws. And this is a big problem. Generating a fair unbiased random number is critical. In fact, random number generators are used everywhere.
The first place many would think of random numbers being useful is in games of chance. But would you be surprised if you knew that reading this article required the use of a random number generator? The website hosting this article is protected by a cryptographic key, which relies on generating a random set of values to be used for the encryption key.
Generating numbers at random is difficult. At a high level, there are two main issues with generating random numbers: predictability and bias/corruption issues.

The predictability issue for RNG can be seen in both human- and machine-generated random numbers. For example, there is a famous problem called Benford’s Law that states any random number that someone thinks about has a 30% chance of starting with the number 1. When you want to have a chance of a number being generated to be equal in percentage, then this becomes a problem. If you use a computer program to generate random numbers, you are using a structured code. This means, after multiple iterations, someone can reverse engineer the numbers to find the pattern and predict what the next number could be, especially if the code being used is weak.
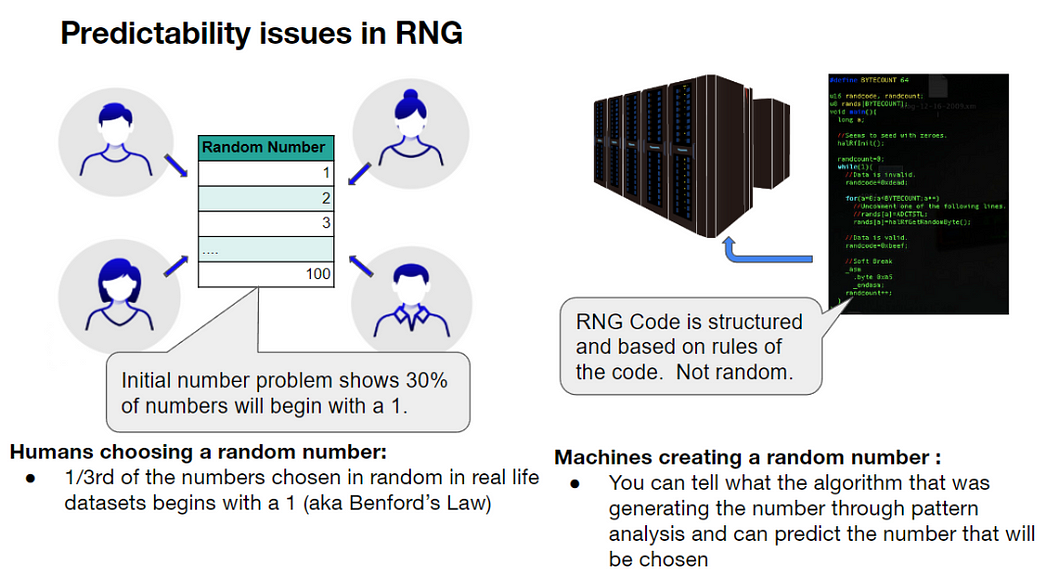
From a bias and corruption perspective, the current systems can also be gamed to give favor to someone. For instance, if a set group of people decide they will choose random numbers and run through some function to compute a random number, one person may withhold showing their number until they see what the other people have chosen. Then, once he knows the numbers of the other participants, he can choose a number that would compute the random number to his favor. From a machine generated random numbers, since most systems have a central system that is generating the numbers, anyone who has control of that system could also manipulate the numbers being generated to their favor.

So how can we create a system where it is both unpredictable and bias free? Through MPC and Partisia Blockchain, we can solve both problems. Through smart contracts, players in the system generate a random number. This random number is then privatized and sent into the PBC blockchain. A zero-knowledge computation is done, in a similar way as done through secret sharing and through a computation, a random number is revealed.

Through combining multiple players and secret sharing, developers can create a system to come up with a random number that is free from bias, incorruptible and impossible to predict. And Partisia Blockchain’s smart contract language will afford developers to customize this solution to their specific requirements.
By creating a programming language that allows for developers to use MPC in a generic way, Partisia Blockchain Foundation has made the creation of applications that can harness the power of MPC for different use cases a possibility. Partisia has been at the forefront of providing private MPC solutions since 2008. And by layering this technology on top of an interoperable and scalable blockchain, Partisia Blockchain is now paving the way for anyone to create solutions that can balance privacy and transparency to build trust.
To learn more about different use cases or partner with us for solutions, please visit partisiablockchain.com, check out our Medium articles, development documentations or email us at build@partisiablockchain.com.
Trust is the basis for any relationship. Whether it is between you and your friends, or between one company working with another, even with governments sharing information with each other. Without trust, society cannot exist. Every type of a relationship requires some type of trust that is built through time.
But what is trust? And how does one go about establishing it with another entity? Trust is earned through a give-and-take between parties and demonstrated pattern of reliability. It is also relative, as everyone has a different level of risk appetite. A balance that is relative to the amount of risk the person is willing to take against the amount of reliability the other party has demonstrated in the past.
So how does this balance take place?
Clearly, if no one is willing to share or demonstrate anything about themselves, trust cannot be established. There has to be some level of vulnerability to even begin the initial stages of establishing trust. But at the same time, complete and full transparency also does not help establish trust. And this is because almost all relationships start off mutually distrustful. Trust is something earned. If given to someone arbitrary, that person could use that trust against you.
And in a way this balance of privacy and transparency to establish trust has been tipped in favor of one side to another throughout history. How many times have you or someone you know been burned by giving trust to someone who–knowingly or unknowingly–betrayed it? How many deals are broken between companies? How many government secrets have been compromised through leaks? Building trust is a gradual process, where one party shares something in hopes that the other party shares something of equal value.
But what if there was a way to share information without sharing information?
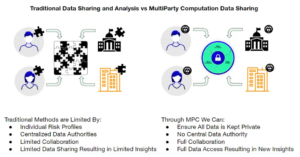
As we reviewed in other articles, multiparty computation allows for the computing of data even if the owner does not share the details around it. And in the example of sharing of data, this means any mutually distrustful parties can collectively allow the use of their data without sharing the details of data itself.
What does this mean in practice? At a high level, this means you can now reduce the weight of risk in the balance of establishing trust. Because you no longer have to expose your private data, the risk of that data being used against you is lowered. And this means you no longer require the same heavy weight for demonstrated reliability that you would need on the other side of the trust scale.
This is a game changer on many levels. Trust is the fundamental basis for any relationships between entities. With MPC, we now have the opportunity to change how this can be played.
In the example below, let’s say we have two financial companies that are competitors. They have a lot of secrets they would like to keep internal, but they do business with each other as a part of their overall practice. As a result of their business, there are many mutual clients. If there was a suspicious activity in one of their clients, having a single set of data they can analyze may not be enough. But what if both companies could share the use of their data together for forensic analysis without sharing the details of the data itself? This may lead to a far more comprehensive analysis.
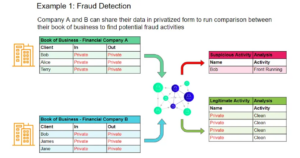
Another example is where multiple companies need to validate meeting of certain regulatory or compliance goals. But to compute the data, it requires exposing private information. Through MPC and Partisia Blockchain, a company will be able to validate meeting regulatory goals without exposing their data to the public.
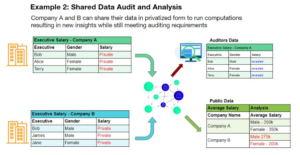
These are very simple examples of how companies can still work together without revealing their private data. And we have quite a variety of projects building on Partisia Blockchain that takes advantage of this new way of doing business.
CyberPeace Institute is working with Partisia Blockchain to help NGOs combat the issue of malware and ransomware by allowing NGOs to privately work with other parties who may be facing similar attacks. This allows NGOs to work together with others without reputation impact or exposing information that may create other vulnerabilities in their system.
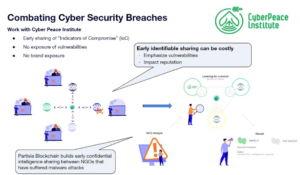
Monadi is working on helping companies comply with CSRD regulations that will impact over 50,000 companies in the EU. By 2025, companies will need to validate that they are meeting certain SDG goals, with the first goal being able to certify that there is no gender pay gap in their executives’ compensations. As the regulation matures, Monadi will be in a good position to help companies certify other SDG requirements without the need for the company to expose private data.

With a growing number of partners and integrators looking to solve the issue of trust, Partisia Blockchain is well positioned to help provide the solutions we need–whether it is to address the transparency in blockchains or to solve existing problems outside the blockchain space.

For additional insights on this use case, come and watch our Q&A session we did on this topic.
By creating a programming language that allows for developers to use MPC in a generic way, Partisia Blockchain Foundation has made the creation of applications that can harness the power of MPC for different use cases a possibility. Partisia has been at the forefront of providing private MPC solutions since 2008. And by layering this technology on top of an interoperable and scalable blockchain, Partisia Blockchain is now paving the way for anyone to create solutions that can balance privacy and transparency to build trust.
To learn more about different use cases or partner with us for solutions, please visit partisiablockchain.com, check out our Medium articles, development documentations or email us at build@partisiablockchain.com.