
We’re excited to share the latest developments, achievements, and ongoing initiatives from March 2025, marking progress on our mission to become the leading platform for interoperable, omnichain data privacy. Here’s a full breakdown of the most important highlights across tech, ecosystem, and marketing:
Q1 Roadmap Delivered:
Foundation Laid for Scale:
Builders Gearing Up:
MPC Tooling Expanded:
zkCrossDEX Nears Launch:
Narrative Emphasized:
Stronger Community Infrastructure:
Strategic Visibility:
Read on to find out more.
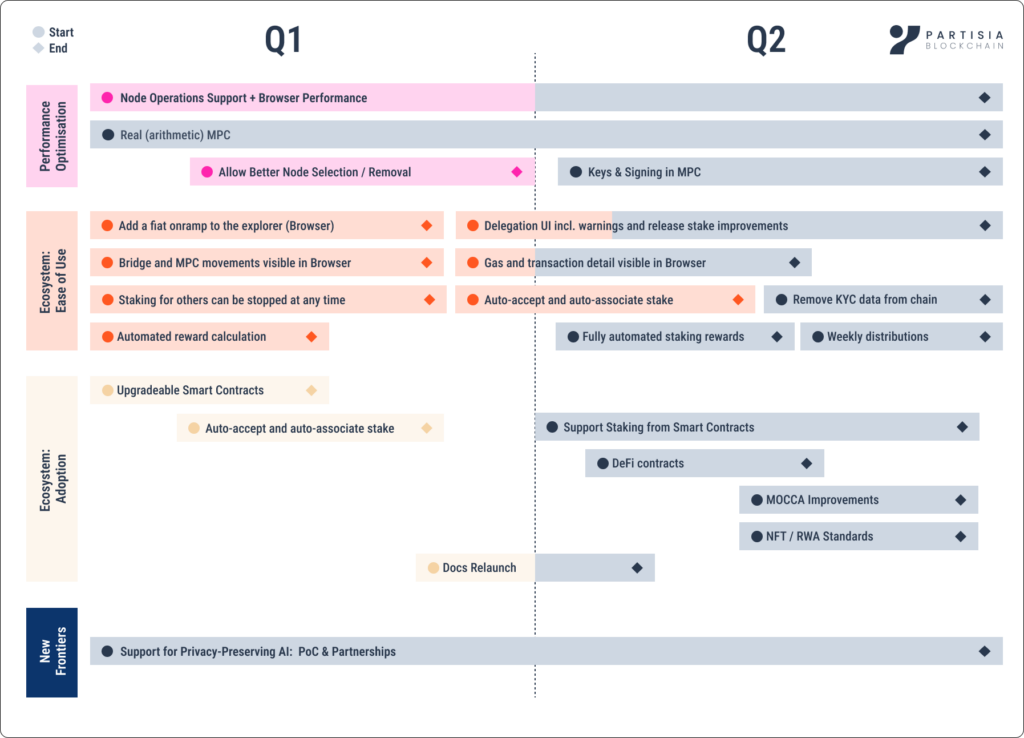
H1 2025 Technical Roadmap Progress
There have been a vast number of developments across the Browser and blockchain itself. Here are some of the key updates completed and in progress:
Our team successfully delivered all the following planned items from the Q1 segment of our H1 2025 Technical Roadmap:
Auto-Accept of Delegated Stakes:
Staking Expiry Management:
Improved Delegation UI & Management:
The delegation interface has been redesigned for clarity and fairness:
Oracle Rotation Capabilities:
ZK Registry Optimization:
WASM Off-Chain Execution:
Banking Overview Phase 2 (MPC Transfer Movements):
Browser Enhancements:
Ongoing work on the Partisia blockchain Browser:
Developer Ecosystem Enhancements:
Banking Overview Phase 3:
Further Delegation UI Improvements:
Stake Auto-association:
ZK Node Testing Enhancements:
The only remaining item from Q1 is the arithmetic MPC upgrade. This has been rescheduled to the end of Q2/early Q3 due to dependencies with our MPC key management solution (which is in high demand).
Development continued actively across several projects:
This mix of native and MPC-as-a-service decentralized Apps (dApps) reflects growing demand across chains for programmable privacy infrastructure.
These projects, and more, are anticipated to continue progressing towards their significant milestones or launches in Q2, underscoring continued momentum towards adoption.
MPC Node App and Partiscan.io simultaneously pushed essential feature updates, greatly enhancing node operator efficiency. The former is available as a mobile app for node operators, however, now they’ve opened access for all Partisia Blockchain users.
You can download the application via iOS and Android today – check it out and make sure to leave a positive review if you like what you see.
In March, we launched a series of blogs to address community questions, define our long-term vision, and clarify our strategic direction. This series served to bring coherence and clarity to the evolving identity of Partisia Blockchain:
A Connected Vision for Privacy, Interoperability, and Real Adoption
Reimagining Web3: A Vision of Privacy, Interoperability, and Real Adoption
Introducing Gods Network: Powering the Future of Web3 and Enterprise Interoperability
The Hybrid Future of Enterprise Blockchain
How Partisia Blockchain Foundation Operates and Collaborates to Drive Public Blockchain Success
Together, these articles provide the narrative structure for the next stage of Partisia Blockchain’s journey — focused on reduced friction, increased adoption, and a platform where privacy and usability are not mutually exclusive.
ETH Denver:
EPFL Panel Participation:
Moving into Q2 2025, our community can anticipate several exciting developments:
We sincerely thank you for your ongoing support and enthusiasm. Stay tuned for further exciting developments and announcements!
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
February, though the shortest month of the year, marked a critical period of consolidation for Partisia Blockchain. Our team dedicated significant efforts to laying the foundational groundwork for upcoming launches, advancing key ecosystem initiatives, and enhancing our technical infrastructure.
This update provides a clear overview of February’s progress, including ecosystem updates, partnership developments, technical enhancements, and insights into upcoming activities.
February’s focus centered around critical preparations for upcoming launches:
The Partisia Blockchain ecosystem continues to mature, with important advancements across strategic partnerships:
Since its soft launch in late January, zkCrossDEX has significantly evolved based on extensive community testing and feedback.
An incentivized marketing campaign, featuring MPC and CROSSAI token rewards, is planned to accompany the full launch. Specific launch dates will be communicated soon, ensuring transparency and realistic community expectations.
Boosty Labs’ lending solution continues progressing steadily, targeting a public launch in the coming months.
Crowdsnap completed private survey implementations successfully on mainnet and is now very close to being ready for public launch. For more details, check out their website.
Koala Wallet will soon introduce private key import functionality, simplifying migration from Parti Wallet. Additionally, the introduction of the Brillion Wallet is expected to complement Koala Wallet, expanding our ecosystem’s wallet infrastructure.
February featured two impactful live sessions with Profila, covering decentralized identity and a live-streamed pitch showcasing their innovative solution. Profila is building on Cardano but leverages Partisia Blockchain’s omnichain confidential compute layer, highlighting our MPC technology’s cross-chain privacy capabilities.
Our team had a strong presence at ETH Denver, co-hosting an impactful MPC-focused hackathon alongside Secret Network, showcasing practical MPC applications and raising our profile in the web3 and privacy-tech community.
Key Highlights from ETH Denver:
Beyond ETH Denver, we also initiated strategic partnership discussions with Oasis Labs and Secret Network to explore potential integrations combining MPC with Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) technologies.
Furthermore, in response to the recent Safe wallet (Bybit) breach, we proactively highlighted our MPC On-Chain Custody solution as a secure and superior alternative to traditional custodial methods, reinforcing our position as leaders in blockchain security.
In February, our technical team delivered crucial updates enhancing stability, usability, and developer experience:
In addition to the above, we also delivered four key roadmap features planned for the first half of 2025.
Further details can be found here.
As we approach the end of Q1 2025, several significant milestones are on the horizon, including major launches, marketing campaigns, and reward distributions.
While timelines remain flexible to ensure high-quality deliveries, we anticipate:
Thank you for your ongoing support. We look forward to celebrating these milestones and sharing more exciting developments with you soon!
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube

In a thriving blockchain ecosystem, clarity and synergy are paramount. Our multi-entity design ensures that each organization contributes unique expertise while remaining laser-focused on strengthening the public blockchain.
This approach—where independent companies collaborate under the governance of Partisia Blockchain Foundation (PBF)—is a proven model seen in other blockchain ecosystems, such as Cardano’s relationship with the Cardano Foundation, IOHK, and EMURGO.
By upholding financial independence, robust governance, and a shared commitment to the success of PBF, we guarantee that every initiative ultimately serves the Partisia Blockchain community—driving adoption, innovation, and long-term success for the public network.
To provide a clear understanding of how these entities work together, here is a high-level breakdown of their roles:
Each of these companies operates independently but plays a distinct role in strengthening the public blockchain ecosystem under the governance of PBF. Below, we provide a more comprehensive overview of their contributions and governance structures.
At the core of the ecosystem is the Partisia Blockchain Foundation (PBF), a Swiss non-profit entity responsible for governing the public blockchain’s development, adoption strategy, and ecosystem growth. The foundation is the guardian of the public blockchain, ensuring that it remains open-source, transparent, and accessible for developers, enterprises, and the broader web3 community.
PBF was established in 2020, following an extensive regulatory process to ensure compliance with Swiss financial authorities and alignment with utility token regulations. This regulatory foundation remains a key pillar of the project’s long-term legitimacy and governance.
PBF follows a strict governance model, supervised by the Swiss ESA and is subject to rigorous audits and financial oversight. It operates under a locked-purpose structure, meaning its funds can only be used to develop, promote, and bring the public Partisia Blockchain to market.
The development of Partisia Blockchain dates to March 2017, when the first lines of code were written by Partisia Infrastructure (PI). PI played a critical role in shaping both the technical architecture and regulatory framework, ensuring compliance with Swiss utility token regulations. The early development efforts culminated in Version 1.7, which was acquired and open-sourced by PBF in October 2020, leading to the public release of Version 2 in January 2021.
The Foundation plays a crucial role in strategic planning, ensuring that the blockchain evolves in line with its mission. The original roadmap was set out in the whitepaper, with a yearly roadmap review that is subject to quarterly replanning. The latest iteration was a 6-month roadmap, completed in January 2025.
Although independent companies like PI and GN Solutions (GN or GODS Network), contribute to blockchain development, PBF remains the governing entity, ensuring that public blockchain progress remains transparent, decentralized, and independent from private interests. As governance continues to evolve, efforts are underway to explore more community-driven governance models.
While PBF remains the central governing entity of the public blockchain, several independent companies contribute technical expertise, adoption strategies, and infrastructure. Below, we outline their roles and how they align with PBF’s mission.
Partisia Infrastructure (PI) is an independent Danish company specializing in blockchain solutions, encryption, and privacy-preserving cryptography. However, its role in the ecosystem goes beyond enterprise applications—it has been a driving force behind the technical foundation of the public blockchain since its inception.
Partisia Infrastructure (PI) is the dedicated core developer team and technological brain trust behind the public blockchain. With over a decade of expertise in advanced cryptography, multi-party computation (MPC), and blockchain technologies, PI played a pivotal role in shaping the public blockchain’s whitepaper, regulatory framework, and token classification. As part of a larger group of independent Partisia companies that existed long before the blockchain’s launch, PI operates independently, generating its own revenue through private-sector contracts and projects ranging from quantum computing security to MPC-based key management (via Sepior, now a Blockdaemon company).
PI was responsible for building the core mainnet protocol, leveraging its deep cryptographic expertise to ensure a secure, scalable foundation for the blockchain. This work was delivered at a heavily discounted rate, underscoring PI’s commitment to the success of the public blockchain.
Since then, PI has remained the core development company behind the public blockchain, responsible for:
Beyond development, PI also plays a key role in enterprise adoption, acting as a go-to-market (GTM) partner for businesses transitioning to web3. By working with enterprises on private blockchain solutions, PI is often able to guide them toward the public blockchain, increasing on-chain activity and adoption.
Despite its involvement in development and enterprise solutions, PI operates independently from PBF, with strict governance ensuring that no public blockchain funds are used for private enterprise projects.
GODS Network is a Swiss-based entity established by Partisia Group—the same company that owns Partisia Infrastructure. It was created to solve a major challenge in web3: fragmentation across blockchain ecosystems.
By acting as an interoperability layer built directly on Partisia’s public blockchain, GODS Network connects disparate blockchains into a unified, seamless infrastructure, allowing data and transactions to flow across networks effortlessly.
At its core, GODS Network functions as a decentralized data subscription layer, enabling any smart contract on any blockchain to publish and subscribe to data across chains. This removes the silos between EVM and non-EVM blockchains, making decentralized applications more accessible and functional. The integration also enables Partisia’s public blockchain to provide privacy-preserving computation as a commodity across multiple chains, offering a unique value proposition in the web3 ecosystem.
While GODS Network is built by Partisia Infrastructure, it operates as a completely independent entity. It receives no funding or grants from Partisia Blockchain Foundation (PBF), ensuring a clear financial separation between GODS Network and the foundation. However, there is close collaboration between GN and PBF on business development, ensuring that GODS Network’s innovations directly drive adoption for the public blockchain.
One of the most significant benefits of GODS Network is that any use of its interoperability features will generate on-chain transactions on Partisia Blockchain. This means that while GODS Network operates independently, its success directly contributes to network activity and revenue generation for Partisia Blockchain node operators. By bridging blockchains and enabling seamless cross-chain transactions, GODS Network is positioned to be a key driver of Partisia Blockchain’s adoption in the broader web3 space.
PBC Apps is a Cayman Islands-based company founded by Brian Gallagher, a former co-founder and previous member of the Foundation Council. As part of the natural evolution of the ecosystem, Brian stepped away from day-to-day involvement with the foundation, shifting his focus to external adoption initiatives outside of PBF.
Originally, PBC Apps played a key role in driving early web3 adoption on Partisia Blockchain, leveraging its expertise to support ecosystem growth and infrastructure development.
The company was engaged in an arm’s length development agreement to build and maintain core ecosystem tools, including the initial explorer and Parti Wallet, which was—until recently—the only available wallet in the Partisia ecosystem.
Over time, the blockchain has expanded beyond a single provider, introducing new wallet solutions and enabling broader developer participation.
Today, PBC Apps operates entirely independently from the foundation and receives no further payments from PBF, originally required to build core infrastructure like wallets. It functions as a third-party service provider, just like any other independent vendor in the ecosystem, with no exclusivity or preferential treatment. This transition reflects the maturity of the public blockchain ecosystem, moving towards a more decentralized and competitive infrastructure landscape.
Ensuring strong governance and alignment between all companies in the ecosystem is a key priority for the Partisia Blockchain Foundation (PBF). The focus is not just on legal compliance, but on ensuring that every entity involved operates in a way that benefits the public blockchain and serves the long-term vision of the ecosystem.
From the very beginning, PBF was designed with a governance structure that prioritizes independence and accountability. Before the foundation was formally established, the co-founders worked extensively with Swiss regulators to ensure that the blockchain’s design met Utility token regulatory standards. This regulatory groundwork—combined with the development of the initial network version and the publication of the whitepaper—laid the foundation for how PBF would be structured.
To ensure that development efforts remained aligned with the public blockchain’s success, arms-length agreements were put in place with both Partisia Infrastructure and PBC Apps. These agreements were carefully structured and reviewed by an independent third party, ensuring that any services provided by external entities adhered to market standards and fair governance principles.
As PBF continues to evolve, governance remains an area of active development and refinement. The foundation operates under strict Swiss ESA supervision, undergoing annual audits that have consistently resulted in high compliance rankings with no critical issues. However, beyond regulatory adherence, the real measure of good governance is whether the relationships between entities in the ecosystem ultimately benefit the public blockchain and its stakeholders.
Instead of forcing a premature shift toward decentralized governance, the focus will remain on ensuring that the right governance mechanisms are in place to support the blockchain’s long-term success. As part of this commitment, the foundation’s council is actively exploring options to move toward a more community-centric governance model, including community representation on the council and a DAO model. These avenues would ensure that the public blockchain’s governance becomes more decentralized, balanced, and inclusive, with stronger representation from the community.
While the governance structure will continue to evolve over time, these options aim to strengthen transparency, accountability, and community involvement in decision-making. Should a clear route, requirement, and environment for these ideas arise in the future, it will be driven by community demand rather than imposed as a governance model for its own sake.
Governance improvements will be introduced gradually, ensuring that shifts toward decentralization are well-planned and beneficial to the network.
The Partisia Blockchain Foundation (PBF) is committed to building a sustainable, high-impact public blockchain. The separation of roles and responsibilities allows each organization to focus on its core strengths, ensuring that PBF remains dedicated to governance, adoption, and ecosystem growth while benefiting from technical expertise, interoperability advancements, and infrastructure contributions from aligned entities.
The public blockchain remains at the centre of this ecosystem, and PBF continues to explore opportunities to evolve its governance model to increase community involvement.
Partisia Blockchain is entering a new phase of growth, accountability, and execution, and we are excited to move forward together with the community toward a stronger, more decentralized future.
Dive deeper into the other relevant topics here:
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube

In today’s fragmented web3 landscape, hundreds of blockchains operate as isolated silos—each with its own language, protocol, and consensus. This complexity creates daunting challenges for developers, enterprises, and users, hampering innovation and impeding secure, seamless data exchange. True interoperability remains the holy grail of web3.
GODS (Global Omnichain Data Service) is a breakthrough interoperability protocol that transforms complex cross-chain interactions into a simple, secure, and cost-effective subscription service. By enabling decentralized applications (dApps) to “listen” to events across diverse blockchains, GODS Network empowers innovation, drives enterprise integration, and fuels the growth of the Partisia ecosystem—all while upholding the vision of a decentralized, user-centric future where privacy and data control are paramount.
GODS Network envisions an “Internet of Blockchains” where data and assets flow effortlessly between networks. Its mission rests on three key pillars:
1. Breaking Down Barriers:
2. Transforming Interoperability
3. Security & Trust
Think of GODS Network as a universal remote control that can work with any device in your home – eliminating clutter and complexity. That is the promise of GODS Network for web3:
Every operation—from subscription initiation to MPC validation—is recorded on the public Partisia Blockchain. This transparency builds trust and allows anyone to audit the system in real time.
Distributed key management among a large number of MPC nodes means that even if some nodes are compromised, the integrity of cross-chain transactions remains intact. This state-of-the-art approach reduces the risk of a single point of failure.
Acting as a universal translator, GODS seamlessly connects EVM-based chains like Ethereum with non‑EVM chains such as Partisia Blockchain, Cardano, and Solana. Developers can integrate data from multiple sources without juggling different codebases or SDKs.
Much like calling a familiar API, developers can easily subscribe to on-chain events without writing complex bridging logic. This simplicity accelerates development and reduces operational overhead.
With a pay‑as‑you‑go model and the use of Merkle tree proofs to batch updates, GODS significantly lowers gas costs—a major advantage for high-frequency applications.
As the web3 landscape matures, interoperable data and assets become increasingly critical. Here are some real-world applications that demonstrate GODS Network’s transformative potential:
Many enterprises are eager to explore web3 but are slowed by complexity and fragmentation. GODS Network functions as a secure, transparent decentralized API that bridges legacy systems with modern blockchains. Imagine a supply chain platform where internal logistics run on a private network while payment settlements occur on multiple public blockchains—the integration made effortless by GODS Network.
Think of GODS Network as the API that connects secure enterprise systems with the decentralized world—a solution that bridges legacy and innovation seamlessly.
GODS Network is a critical pillar within the broader Partisia Blockchain ecosystem, reinforcing our shared vision of a decentralized, privacy-focused future:
Bridging Public and Private Networks
Driving On-Chain Activity
A Synergistic Ecosystem
At Partisia Blockchain, our vision is to reimagine web3 by “doing for data what Bitcoin did for money.”
We are committed to creating a decentralized network where privacy, interoperability, and real adoption coexist. GODS Network is the embodiment of that vision—an innovative interoperability layer that transforms a fragmented landscape into a unified digital infrastructure.
GN Solutions AG (the company behind GODS Network) is a Swiss-based entity established by Partisia Group—the same organization behind Partisia Infrastructure. Created to address the fragmentation of blockchain ecosystems, GODS enables any smart contract on any blockchain to publish and subscribe to data seamlessly.
Although built by Partisia Group, GODS operates independently and receives no funding or grants from the Partisia Blockchain Foundation, ensuring clear financial separation while benefiting from close business collaboration.
Every use of GODS Network’s features generates on-chain transactions on Partisia Blockchain, contributing to network activity and revenue. In this way, GODS plays a key role in advancing the broader web3 ecosystem while maintaining its distinct identity.
Read more about the different entities within the Partisia ecosystem here.
GODS Network offers a compelling vision for the future of blockchain interoperability. By transforming cross-chain data exchange into a secure, subscription-based service, it empowers developers, accelerates enterprise adoption, and drives the growth of the Partisia ecosystem.
Together with Partisia Blockchain’s commitment to privacy and robust cryptography, GODS Network is poised to make a fragmented landscape truly unified and accessible.
We hope you enjoyed our introduction and exploration of the potential of GODS Network.
Stay tuned for more updates and join our upcoming AMAs to learn more about how GODS Network is powering the future of web3 and enterprise interoperability.
Dive deeper into the other relevant topics here:
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Blockchain technology is widely heralded as a transformative force for enterprise – from streamlining supply chains and enhancing financial processes to securing digital identities. It promises to radically improve how organizations manage data, trust, and transactions. Yet, many enterprises remain cautious about fully embracing public blockchain solutions because of concerns around security, scalability, privacy, control and regulatory compliance.
A compelling answer lies in a hybrid blockchain model – one that combines the best aspects of private (permissioned) and public (permissionless) networks. By integrating the control and confidentiality of private systems with the transparency and decentralization of public chains, enterprises can safeguard sensitive information while benefiting from global trust and interoperability.
Coupled with advanced solutions like the GODS Network, this approach not only addresses critical enterprise challenges but also drives broader public chain adoption.
It is important for us to outline what private and public blockchains are. This sets the groundwork for understanding why a hybrid model is best suited to catalyse enterprise adoption for the public blockchain network.
Characteristics:
Drawbacks:
Examples in practice:
Characteristics:
Drawbacks:
Examples in practice:
Think of a traditional bank. You access your account via a public app over a public network, but behind the scenes, the bank’s internal systems are protected by a secure intranet. Sensitive data like HR records or proprietary processes remain hidden, while only essential transaction data (like your account balance) is visible externally.
In web3, a private blockchain functions as this intranet, allowing sensitive computations to be kept confidential. Meanwhile, key outcomes—such as transaction confirmations—can be recorded on a public chain, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Large organizations often balk at placing any data on a fully public ledger—even if encrypted—due to regulatory constraints, internal policies, control, and privacy concerns. By offering a private network that seamlessly interfaces with a public chain, enterprises can:
It might seem counterintuitive, but as enterprises deploy private blockchains to manage sensitive data, they naturally generate key events—such as transaction finalizations—that can be recorded on public chains for greater transparency.
These on-chain records not only verify the private process but also bring real-world validation and transaction volume to the public ecosystem. Over time, this interplay boosts the credibility and adoption of public blockchains while enterprises get comfortable on the private side.
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) is a critical technology that enhances security by allowing multiple parties to compute functions over their data without revealing the inputs. In a hybrid model:
Decentralized MPC:
Centralized MPC:
Hybrid MPC Approaches:
GODS Network further the migration from enterprise blockchains to any public blockchain by not locking migration to a single public blockchain. It’s designed as a cross-chain data subscription layer that seamlessly connects disparate blockchains—whether private or public—through a simple, API-like interface. Here’s what makes GODS Network unique:
A hybrid blockchain model is the most practical solution for onboarding web2 enterprises into the web3 world. By keeping sensitive data and internal processes on a private network while using public chains for key transactions, enterprises can:
As enterprises increasingly migrate to hybrid frameworks, they generate a wealth of validated public transactions that enhance the overall credibility and interoperability of blockchain networks. Platforms like GODS Network embody this vision by offering a secure, scalable, and developer-friendly bridge that not only protects sensitive data but also catalyzes broader public chain adoption.
The journey toward enterprise blockchain adoption has been deliberate and measured, with enterprises seeking solutions that balance privacy, control, and regulatory compliance against transparency and decentralization. Hybrid blockchain models effectively bridge this gap by combining the best elements of private and public blockchains, delivering secure, scalable solutions that enterprises can comfortably adopt.
The banking analogy illustrates how internal systems (the “intranet”) can coexist with public interfaces, enabling both confidentiality and auditability. GODS Network enhances this hybrid approach by seamlessly connecting private and public infrastructures, streamlining cross-chain interactions and simplifying overall user experience. It is an essential tool for facilitating smooth integration and interaction.
As enterprises build confidence in this hybrid model, they will drive increased public chain activity, ultimately creating a robust, interconnected web3 ecosystem.
Dive deeper into the other relevant topics here:
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube

Web3 is widely described as the next evolution of the internet, a decentralized, user-centric ecosystem where individuals control their digital assets and data.
Yet, while blockchain technology delivers transparency and asset ownership, true data control remains elusive. People may hold and control their assets on-chain, but they generally lack privacy over how their personal information is stored, shared, and monetized.
At Partisia Blockchain, we fix this. Our mission is to embed privacy and data ownership in Web3 through Multiparty Computation (MPC)—a powerful cryptographic technology that enables secure, centralized privacy-preserving computations.
This is why we say: “We do for data what Bitcoin did for money.”
Our vision is clear: build a decentralized network that is both transparent and confidential, enabling users and organizations to interact freely without losing control of their data.
Achieving this requires removing friction, enabling seamless interoperability, and delivering a practical path for both native web3 projects and traditional enterprises to build on or with Partisia Blockchain.
To bring this vision to life, our strategic priorities focus on two key areas:
Despite remarkable strides in the blockchain industry, widespread adoption is still hindered by fragmentation, inefficiencies, and insufficient confidentiality.
Partisia Blockchain tackles these challenges in several ways:
User-centric confidentiality and data control:
Cross-chain interoperability:
Scalability and stable fees:
Which enables many new and novel use cases such as:
Bringing Privacy to DID and AI:
Providing Cross-Chain MPC Security:
Enhancing Cross-Chain DeFi:
Although Partisia Blockchain is a best practice L1 it does not compete with other L1 or L2 projects; instead, we complement them. We do so by providing privacy, security, and cross-chain functionality that makes web3 more scalable, user-friendly and secure.
For enterprises, the leap into decentralized technology can be often seen as too daunting, complex and disruptive. Many factors may contribute to this, including concerns around security, scalability, privacy, control, and regulatory compliance.
Partisia Blockchain simplifies this process by providing a step-by-step migration path that allows businesses to transition from private networks to public blockchain ecosystems at their own pace.
There is a natural supply chain perspective in moving web2 companies to web3. While industry collaboration typically happens in private enterprise controlled networks, web3 offers a superior way to enhance the collaboration with end users of a product or service.
Two core properties of Partisia Blockchain makes it a pathway to web3:
Examples of enterprise adoption use cases include:
By minimizing adoption hurdles, we empower enterprises to capitalize on blockchain core benefits – transparency, interoperability, and privacy – without disrupting their existing operations.
This strategy is already reflected in our six-month technical roadmap for Partisia Blockchain, merging technical advancements with ecosystem expansion plans.
Strengthening the Developer Ecosystem:
Improved User Onboarding:
Expanding BYOC (Bring Your Own Coin) Solutions:
Expanding BYON (Bring Your Own (zk) Nodes)
Utilizing GODS.Network
A more detailed roadmap update will be shared in June, outlining the next evolution of the project.
One of the most significant innovations in the ecosystem is the launch of GODS Network, a revolutionary interoperability layer built on Partisia Blockchain.
Leveraging MPC and secure cryptographic techniques, GODS Network enables any smart contract to seamlessly access and process data across multiple blockchains—turning fragmented ecosystems into a unified digital infrastructure.
In essence, GODS Network addresses one of web3’s biggest barriers—true interoperability—while amplifying Partisia Blockchain’s vision of a privacy-focused, scalable, and decentralized future.
It is worth noting that GODS Network is funded independently from the Partisia Blockchain Foundation, hence, the Partisia Blockchain benefits from additional throughput and activity without extra cost to the ecosystem.
Learn more via our dedicated introductory article or through the GODS.Network website.
A public blockchain’s long-term success is measured by real-usage, not short-term speculation. Our strategy is designed to drive 3 core pillars:
While we offer grants to builders, we do not rely on them to attract enterprises. They join us for ROI and a robust technical foundation with proven technical expertise to take on this challenge.
Our sustainability model focuses on consistent ecosystem involvement – real transactions, ongoing integrations, and enduring partnerships, rather than token-driven boom and busts.
Decentralized governance is key to fulfilling our long-term vision. The Partisia Blockchain Foundation (PBF) is a Swiss-regulated non-profit, operating under strict oversight to ensure funds are used solely to develop and promote the public blockchain.
Over time, as we evolve, we will implement governance improvements to further align with community participation and transparency. Discussions and updates around governance changes will be conducted through blog posts, social channels, community channels and other avenues we’re working on.
You can join us across any of these channels, available via our linktree.
Our goal is not just decentralization for the sake of optics, but real, functional governance that supports the long-term success of the network.
Governance improvements will be introduced gradually, ensuring that shifts toward decentralization are well-planned and beneficial to the network.
Partisia Blockchain is a key enabler of a truly decentralized web3. By combining MPC-powered privacy, interoperability, and real enterprise adoption, we are setting the stage for a more secure, scalable, and inclusive digital economy.
We are at a pivotal moment in our journey. With a refined strategy, an expanding ecosystem, and clear governance direction, we are ready to take web3 to the next level.
Expect to see major developments in the coming months, including new technical rollouts, ecosystem partnerships, and deeper community engagement.
Dive deeper into the other relevant topics here:
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube

Web3 promises a decentralized internet built around transparency, true digital ownership and user empowerment. Yet, despite significant innovation, widespread adoption remains slow and elusive.
This is primarily due to ongoing challenges like fragmented blockchain ecosystems, inadequate data privacy, and the complexity enterprises face when integrating blockchain into their existing infrastructures – Partisia has been built to solve these problems.
This blog provides an overview of the solutions we’ve built to address these critical barriers:
Blockchain technology has empowered users with asset ownership and control. Yet genuine privacy—control over personal data storage, sharing, and usage— remains limited.
We tackle this head-on with our core innovation: Multi-party Computation (MPC), allowing secure computation without exposing underlying data.
Our vision goes beyond individual empowerment. It’s equally about providing enterprises with secure, compliant, and scalable tools. Enterprises transitioning from web2 to web3 can confidently adopt blockchain technology, leveraging MPC to maintain confidentiality, comply with strict regulations, and gradually integrate public blockchains at their pace.
Here are some of the ways we’re achieving this vision:
The Partisia Blockchain ecosystem is strategically structured to maximise efficiency, collaboration, and effectiveness towards our vision.
At the core of the ecosystem is the Partisia Blockchain Foundation (PBF), a Swiss non-profit organisation responsible for ecosystem governance and adoption.
Surrounding PBF are independent, yet, strategically aligned entities:
This structure, common in mature blockchain ecosystems, enhances collaboration, leverages specialized expertise, and maximizes ecosystem synergy, ultimately fostering a stronger, decentralized ecosystem.
Explore the Entities in our Ecosystem →
Blockchain fragmentation creates unnecessary complexity for developers, enterprises, and end-users. To overcome this challenge, we’re thrilled to introduce GODS Network—a pioneering cross-chain interoperability solution.
GODS Network, developed independently but closely aligned with Partisia Blockchain, provides an intuitive subscription-based data layer, allowing seamless cross-chain communication.
Rather than juggling multiple SDKs and protocols, developers can leverage this simple, subscription-based model to access data across blockchains, including both EVM-compatible and non-EVM chains.
Why GODS Network is a Game-Changer:
Critically, by simplifying and securing cross-chain interactions, GODS Network’s adoption will generate meaningful transaction activity on the public Partisia Blockchain.
Explore the GODS Network in more detail →
Enterprise adoption of blockchain technologies has been slower than anticipated. While regulatory concerns plays a role, businesses often hesitate to embrace public blockchains due to real concerns around exposing sensitive processes or transactional data—even in encrypted forms.
Our hybrid blockchain model offers a pragmatic solution, blending private and public blockchain strengths:
Industry sectors like automotive, finance, and supply chain logistics are already using this hybrid approach in legacy systems. With solutions like GODS Network, combined with private and public solutions bridging these two worlds, enterprises can confidently explore blockchain’s potential while maintaining control over their critical data and processes.
Learn why Hybrid Models are crucial for enterprise adoption →
Our strategy blends powerful innovations in MPC-driven privacy, practical hybrid blockchain solutions, robust cross-chain interoperability via the GODS Network, and a carefully structured, collaborative ecosystem.
As we navigate the next stage of growth, our commitment remains to drive meaningful adoption, not mere speculation—building genuine use cases and providing secure, scalable, and accessible blockchain solutions for everyone.
We invite you to join us on this exciting journey towards a unified, secure, and truly decentralized future.
Dive deeper into each topic here:
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
At Partisia Blockchain, our commitment to continuous innovation drives us to enhance usability, security, and adoption. Our latest technical update delivers four key upgrades outlined in our H1 2025 technical roadmap, reinforcing the foundation for greater scalability, developer flexibility, and a seamless user experience.
These upgrades enhance transparency, efficiency, and developer tooling, strengthening DeFi, enterprise adoption, and beyond.
Read on to learn more about these upgrades, along with some additional exciting elements of our roadmap planned for the coming months.
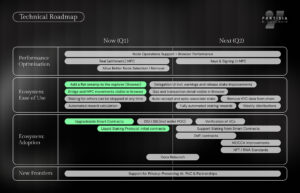
As part of our H1 2025 Technical Roadmap, the following upgrades have now been completed:
Let’s dive into each of these to understand what they mean for users and developers.
Status: Live in Phase 1
Why It Matters: Enhanced transparency & usability
One of the biggest UX improvements for Partisia Blockchain users is the ability to track BYOC (Bring Your Own Coin) movements directly in the Browser.
Key Benefits:
Explore the Update:
What’s Next?
Status: Fully integrated with API Key support
Why It Matters: Seamless fiat-to-crypto access
The integration of Transak into Partisia’s Browser Explorer is a big step toward simplifying onboarding into the Partisia Blockchain ecosystem. Users can now buy MPC directly with fiat, without needing external tools!
How It Works:
Try it out here:
What’s Next?
Status: Open-sourced for the ecosystem
Why It Matters: Flexible staking, improved liquidity
Liquid staking allows users to stake their assets while maintaining liquidity, a feature that has become a standard in DeFi. With this open-source release, developers and ecosystem contributors can now integrate liquid staking into their applications!
Key Benefits:
Want to view the Liquid Staking Contracts? Click here to check out the repo.
What’s Next?
Status: Implemented
Why It Matters: Security, flexibility and long-term usability
While upgradable smart contracts have become an industry standard and critical component in modern blockchains, their addition to Partisia Blockchain unlocks significant improvements for developers and enterprises.
Key Benefits:
What’s Next?
These four enhancements mark a key leap forward in making the Partisia Blockchain ecosystem more accessible, transparent and developer-friendly.
But, this is just the start. In the coming months, we’re rolling out even more game-changing upgrades to push privacy, performance, and usability to the next level:
But, there’s more. Below are a few more items on the roadmap that we’re extremely excited about:
What is it?
Traditional privacy solutions slow things down – but with Real MPC Arithmetic, speed and privacy no longer need to be a trade-off. Building upon our core MPC technology, this advancement enables faster and more efficient secure computations.
Why you should be paying attention!
Think real-time encrypted DeFi, faster private swaps, and scalable enterprise blockchain solutions – all without sacrificing privacy.
What is it?
What if AI could analyze your sensitive data – without ever exposing it? This component of the roadmap will integrate privacy-enhancing mechanisms into AI, allowing for applications that conduct data analysis and machine learning without compromising data confidentiality.
Why you should be paying attention!
Get ready for AI with trustless privacy – keeping data confidential while still allowing AI-powered automation.
What is it?
Imagine a world where you control your identity – without centralized databases tracking your data. DID empowers users with self-sovereign identity solutions and secure key management, enhancing privacy, security and usability.
Why you should be paying attention!
Privacy-preserving, flexible, and built for a decentralized internet. Exciting!
These upcoming features will redefine blockchain privacy, security, and AI-driven trustless automation.
Join us on this journey – make sure to follow us on social platforms and join our extremely passionate community over on Telegram and Discord.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
At Partisia Blockchain, our commitment to continuous innovation drives us to enhance usability, security, and adoption. Our latest technical update delivers four key upgrades outlined in our H1 2025 technical roadmap, reinforcing the foundation for greater scalability, developer flexibility, and a seamless user experience.
These upgrades enhance transparency, efficiency, and developer tooling, strengthening DeFi, enterprise adoption, and beyond.
Read on to learn more about these upgrades, along with some additional exciting elements of our roadmap planned for the coming months.

As part of our H1 2025 Technical Roadmap, the following upgrades have now been completed:
Let’s dive into each of these to understand what they mean for users and developers.
Status: Live in Phase 1
Why It Matters: Enhanced transparency & usability
One of the biggest UX improvements for Partisia Blockchain users is the ability to track BYOC (Bring Your Own Coin) movements directly in the Browser.
Key Benefits:
Explore the Update:
What’s Next?
Status: Fully integrated with API Key support
Why It Matters: Seamless fiat-to-crypto access
The integration of Transak into Partisia’s Browser Explorer is a big step toward simplifying onboarding into the Partisia Blockchain ecosystem. Users can now buy MPC directly with fiat, without needing external tools!
How It Works:
Try it out here:
What’s Next?
Status: Open-sourced for the ecosystem
Why It Matters: Flexible staking, improved liquidity
Liquid staking allows users to stake their assets while maintaining liquidity, a feature that has become a standard in DeFi. With this open-source release, developers and ecosystem contributors can now integrate liquid staking into their applications!
Key Benefits:
Want to view the Liquid Staking Contracts? Click here to check out the repo.
What’s Next?
Status: Implemented
Why It Matters: Security, flexibility and long-term usability
While upgradable smart contracts have become an industry standard and critical component in modern blockchains, their addition to Partisia Blockchain unlocks significant improvements for developers and enterprises.
Key Benefits:
What’s Next?
These four enhancements mark a key leap forward in making the Partisia Blockchain ecosystem more accessible, transparent and developer-friendly.
But, this is just the start. In the coming months, we’re rolling out even more game-changing upgrades to push privacy, performance, and usability to the next level:
But, there’s more. Below are a few more items on the roadmap that we’re extremely excited about:
What is it?
Traditional privacy solutions slow things down – but with Real MPC Arithmetic, speed and privacy no longer need to be a trade-off. Building upon our core MPC technology, this advancement enables faster and more efficient secure computations.
Why you should be paying attention!
Think real-time encrypted DeFi, faster private swaps, and scalable enterprise blockchain solutions – all without sacrificing privacy.
What is it?
What if AI could analyze your sensitive data – without ever exposing it? This component of the roadmap will integrate privacy-enhancing mechanisms into AI, allowing for applications that conduct data analysis and machine learning without compromising data confidentiality.
Why you should be paying attention!
Get ready for AI with trustless privacy – keeping data confidential while still allowing AI-powered automation.
What is it?
Imagine a world where you control your identity – without centralized databases tracking your data. DID empowers users with self-sovereign identity solutions and secure key management, enhancing privacy, security and usability.
Why you should be paying attention!
Privacy-preserving, flexible, and built for a decentralized internet. Exciting!
These upcoming features will redefine blockchain privacy, security, and AI-driven trustless automation.
Join us on this journey – make sure to follow us on social platforms and join our extremely passionate community over on Telegram and Discord.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube