We kicked off the first day in Singapore during Token2049. It is an honor to be a gold sponsor of the 2024 edition and discuss the advancement of the Web3 space during this eventful week. With a full schedule of panels and keynote sessions, here is a recap of today’s major themes:
One of the recurring topics is the institutional interest in blockchain and digital assets. Speakers from major financial institutions emphasized the increasing recognition of blockchain as a tool for improving operational efficiency, transparency, and compliance. The discussions touched on the integration of blockchain into traditional finance systems and the regulatory frameworks emerging across Europe and Asia, especially with Europe’s MiCA and Singapore’s regulatory advancements leading the charge.
DeFi was a major focus today as speakers explored how decentralized financial protocols are revolutionizing traditional banking services. With discussions around liquidity provision, decentralized exchanges, and lending protocols, panelists highlighted the potential of DeFi to enhance financial inclusion while lowering transaction costs. Security and governance within DeFi ecosystems also took center stage, with new solutions being proposed to ensure the stability of these systems as they scale.
During one of the panel sessions hosted by Partisia Blockchain on Level 3, it was discussed that “structured products are the next big thing for DeFi integration, DeFi use work with DeFi if it is going to go mainstream”.
Web3 and its promise to reshape the internet are prominent today. Participants discussed the decentralized internet’s potential to return control of data and assets to users, moving away from the current centralized model. The conversation highlighted how Web3 infrastructure must evolve, addressing challenges related to scalability, interoperability, and user experience before it can achieve mainstream adoption.
Bakyt Azimkanov, Head of Communications at Partisia Blockchain Foundation, reflected on today’s sessions: “We are on the brink of a new era in digital assets and blockchain. The conversations today have shown how institutions and innovators are working together to create a more transparent, decentralized financial system.”
We look forward to sharing tomorrow’s highlights with you.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
August was filled with exciting developments and reflections for Partisia Blockchain. In this recap, we share our upcoming participation as a Gold Sponsor at Token2049 in Singapore, where we will lead discussions on DeFi and Real World Assets (RWA) and the value they bring to the future of our industry. We also highlight the launch of our first mobile wallet, Koala Wallet, which now supports our MPC token across multiple platforms. Additionally, we are now members of the ERC3643 Association, positioning ourselves at the forefront of the RWA tokenization standard setting. We also reflect on key insights from our team members, including Peter Frandsen’s thoughts on data privacy and Bruce Ahn’s perspective on growing the Web3 pie. Dive into the full update to learn more.
We are excited to announce that the Partisia Blockchain Foundation is a Gold Sponsor at Token2049 in Singapore, held at the iconic Marina Bay Sands. Join our team alongside our exceptional partners as we showcase our leadership in DeFi and RWA with thought-provoking speeches, trendsetting panels and interactive booths. On 18–19 September 2024, do not miss our exclusive reDeFining RWA event, where we will explore the future of RWA, DeFi, and multiparty Computation (MPC). No Token2049 ticket is needed to join our event on level 3 in Marina Bay Sands. You can register for Day 1 (18 September) and Day 2 (19 September) here. Stay tuned on our socials to check out the partners we will be bringing along with us. See you there!
Our first mobile wallet, Koala Wallet, developed by Eucalyptus Labs, now supports our MPC token across iOS, Android and browser extensions. The next step is to integrate this wallet into various applications, with browser integration and upcoming DeFi applications set to roll out next month. For detailed instructions on how to add MPC tokens, be sure to check out this link.
Partisia Blockchain Foundation is now a contributing member of the ERC3643 Association. As part of this group, we will actively shape the future of this standard. We believe RWA is key to expanding the Web3 ecosystem, and our role in the Association cements our credibility as a key player in this space. During our AMA with Luc Falempin, Director at the ERC3643 Association, the team touched upon the various critical components of RWA, going beyond simple tokenization and the role Partisia Blockchain will play in helping to push the standard forward. You can watch the AMA here.
Last month of the summer saw an increase in publicity with Partisia Blockchain being mentioned in a number of media outlets. A few highlights include a Crypto News op-ed about bringing transparency into the fundraising process and measuring a direct impact of charities. The piece further highlights our joint efforts with the likes of the Elton John AIDS Foundation and Health Innovation Exchange to trace the impact of donations through the Partisia Blockchain-powered Vorne platform. Partisia Blockchain also made it to CoinMarketCap’s list of Top Staking Rankings. CryptoNews and NewsBTC highlighted our integration with Koala Wallet. Shirly, Mathias and Bruce Bruce were on various X Spaces to engage with the wider audience on a variety of topics, including products, AirDrops, DEX progression, our launch of the mobile wallet and other topics. Listen to both AMAs here and here.
In early August, our Chief of Growth, Shirly Valge, had an insightful engagement at BlockStart in Glasgow on 1–2 August. She took the stage to engage in panels discussing the challenges of managing global Web3 regulations and the transformative potential of tokenization in democratizing access to real-world assets. It was an inspiring event filled with valuable discussions on the future of Web3 and blockchain innovation.
In August, our Co-Founder, Peter Frandsen, shared his thoughts on a pressing issue: how to share confidential data between organizations while maintaining privacy. In his blog, Peter explores how MPC technology is transforming data collaboration, ensuring security without compromising privacy. Dive into his insights on the future of data-driven decision-making here.
Mathias Glintborg, our Head of Product, explores how Partisia Blockchain is enhancing Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) by integrating secure multiparty computation (MPC) and blockchain technology. He discusses how MPC addresses key challenges, such as private data activation, secure storage and privacy in SSI, offering a more complete solution than current models. This innovative approach not only improves data privacy and verification, but also opens up opportunities for compliant data analytics and private AI. SSI builders can leverage this cutting-edge technology, with support and grants available from Partisia Blockchain to help launch the next generation of digital identity solutions. Bruce Ahn also reflected on his recent meetings and conferences. In his opinion piece, Bruce discusses the urgent need to expand the Web3 ecosystem by introducing real-world use cases and engaging new users. His reflections offer his insights into how the boundaries of blockchain technology can be pushed. Explore Bruce’s thoughts here.
We are excited to announce that in September 2024, we will distribute our next set of staking rewards—the largest to date! Over 3 million $MPC tokens will be distributed. Make sure to stake your tokens now to participate in this upcoming reward period and maximize your returns.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
In previous articles we have discussed how secure multiparty computation (MPC) and public blockchains can enhance digital identity for verification and self-sovereign identity (SSI) in particular.
It is now time to take a deeper look into how Partisia Blockchain and its MPC capabilities enhances SSI to cope with the unsolved challenges around private data activation.
This is a great opportunity for SSI builders to pick up cutting edge privacy technology and leverage our support to launch the next billion dollar digital identity business.
For the best teams, we offer grants and dedicated support directly from our core team. Apply for grants here.
Now, let’s get into it!
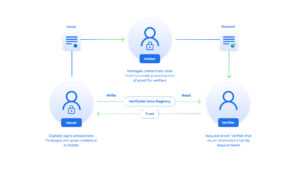
SSI revolves around issuers such as KYC providers that issue verifiable credentials (VCs) to users who store the identity data on their own hardware – therefore “self-sovereign” – typically in an identity software wallet on the phone. Verifiers are the third-party who can receive various types of identity data presentations from credentials such as proof of country and birthdate from a KYC credential. Presentations of VCs is the equivalent of showing physical credentials such as a passport, but in a digital and secure manner.
Presentations are generated in identity wallets by the users themselves and the exchange of them are facilitated by a secure connection that is often managed by a centralized service called an agency.
The idea about SSI becomes really powerful when users receive and hold multiple VCs from multiple issuers that make up entire digital identities, which is entirely owned and managed by the user at first. The complete identity data simply will not rest anywhere else besides on the users own hardware, until the users chose to present the data which in addition can be protected with privacy features such as selective disclosure and zero-knowledge proofs e.g. you only show jurisdiction and prove that you are more than 18 years on from a complete KYC credential that contains much more information than what’s needed for the verifier.
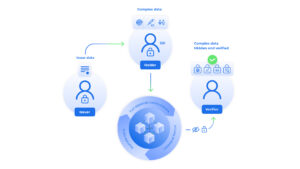
 Notably, VCs are inherently more secure than traditional credentials, such as physical driver’s license, because digital signatures make them tamper-resistant and instantaneously verifiable. Moreover, VCs are digital, portable and reusable, which cuts cost and makes everything much more convenient for users.
Notably, VCs are inherently more secure than traditional credentials, such as physical driver’s license, because digital signatures make them tamper-resistant and instantaneously verifiable. Moreover, VCs are digital, portable and reusable, which cuts cost and makes everything much more convenient for users.
However, as much as SSI offers users true ownership of identity data, it also poses challenges in regards to privacy and compliance when activating the data through presentations for verifiers, backup and storage.
In its current form, SSI does not have strong enough privacy when activating the data through presentations because once a VC has been presented to a verifier, regardless of using privacy features such as selective disclosure and zero-knowledge proofs, the data rest with the verifier in a black box that users cannot control. How data is handled from there would rely on trusting the verifiers to comply with regulations such as GDPR, potential auditing from authorities, and any specific agreements with the users. Furthermore, there is a lack of frameworks and standards for compliant, provable and transparent data monetization which is needed to encourage mass adoption.
Another major issue with SSI in its current form is that users are only left with two options for backup of identity data that either compromise security or privacy. One option is to backup and store identity data on another piece of self owned hardware resulting in multiple self-sovereign controlled backups. However, in reality, this is not convenient for users and if hardware is lost, so is the data.
The second option, which is by far the most convenient and popular, is to store identity data externally with a third party, such as a cloud service. This way, users will unlikely lose the data itself and can always access it. However, relying on centralized external services can result in compromising privacy and giving up control because there’s little transparency in how data is stored and manipulated.
Another profound problem with SSI in its current state is the reliance on intermediaries, often known as agencies or agents, to establish connections between parties and facilitate the exchange of VCs.
Partisia Blockchain has as the world’s first L1 operationalized MPC for general computation on a public blockchain, which means that one or multiple data sources can allow others to compute on the data while it stays encrypted and operate under predefined rules expressed in smart contracts. This is also known as confidential compute and several privacy enhancing technologies (PETs) share this capability. However, MPC is superior when computing on multiple inputs and quantum resistance is a hard requirement.
Confidential compute opens up an ocean of new use cases such as private voting, RWA ownership verification, supply chain provenance, GDPR compliant data analytics across multiple data silos, and very importantly for this article enhanced and complete privacy in SSI.
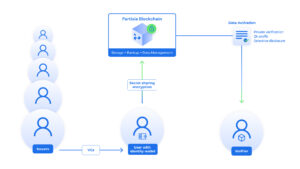
Partisia Blockchain and its MPC capabilities allows a user with an identity wallet to encrypt identity data with secret sharing encryption and then share it with a network of MPC nodes that will not be able to read the original data because the secret shards are distributed amongst the network. There is simply no way to reconstruct the secret and read the original data unless individual secret shards are collected based on a threshold, which is protected by MPC and a collateralized non-collusion security model. Furthermore, secret sharing encryption is by default quantum resistant, so it is not possible to brute force a secret with a supercomputer unlike other PETs like fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) that relies on public key encryption.
This also means that MPC allows for users to have data stored in a “self-sovereign” external network which can function as back-up or simply storage, but more importantly, a private SSI platform to activate the data against a verifier’s request through private verifications and standard privacy features. Partisia Blockchain natively supports multiple standards and can produce presentations for private verification, but also across private and public blockchain for various purposes.
Private verification is really what sets MPC enhanced SSI apart from the current SSI e.g. during the recent pandemic, many attempts were made to create a Covid-19 passport so citizens could prove they were either vaccinated or tested negative while preserving privacy in the claim. Zero-knowledge proofs are good for this, but limited to only presenting yes/no results to a verifier without extensive physical verification, such as ID cards, which would compromise SSI principles.
In collaboration with HES-SO Valais-Wallis, Partisia Blockchain developed a solution where identification is reduced to matching an individual’s face with an image of the person’s face powered by MPC in order to increase security and privacy. The Partisia Blockchain ensures trustworthy information is broadcasted to the verifier and MPC ensures that the private information about the citizen is used only for matching and kept hidden for the verifier.
While MPC is powerful for verification, the idea about having identity data in a private secure network is also useful for use cases that revolves around private AI, e.g. identity data can remain encrypted while a private AI model compute on it and only when the user received the output it can be decrypted incl. the result from the AI model.
Very significant for the above solutions is that the agency is left out so the secure connections and data presentations are managed directly from the MPC clusters where the data privacy is protected and data managed completely on the users’ terms.
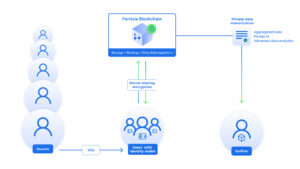
As aforementioned, MPC is powerful when it comes to computing on multiple inputs while preserving privacy. This unlocks a massive potential for compliant and private data analytics on multiple users data combined for use cases such as healthcare data for pharmaceutical R&D and data aggregations for monetization where users are rewarded, but didn’t give up privacy.
The concept is the same as for a single user data where secret sharing encryption is performed and the secret shards are distributed to MPC clusters. However, for multiple users the MPC nodes are able to combine and compute on the data while never understanding the complete input and share encrypted outputs which can only be decrypted and understood by selected users as predefined in zk smart contracts.
DID/SSI is a large stack of different technologies and this article has only covered how to enhance SSI which is the lacking component to offer compliant end-to-end solutions on top of the existing stack. Together with our partners, we are also building out a significant amount of the fundamental DID/SSI component such as agency, mobile SDKs, identity wallets, standards, DID method, DID resolvers, onchain DID documents, definitions and schemas, trusted registries and more.
Reach out to us for a conversation and learn more about our technologies.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
As a part of my role at Partisia Blockchain Foundation, I meet a large number of interesting people at various conferences and events. Some are in Web3 in nature and others are more institution based. And I find there is a difference between these two types of people that highlight what I think is one of the biggest challenges in Web3 currently.
In Web3 conferences, I’m usually meeting the same people I met year after year.
My recent trip to Malaysia and Germany showed this phenomenon clearly. During the Malaysia Blockchain Week, I met with Web3 people who were all in the industry for many years working on similar projects as they were last year. On the other hand, outside of the blockchain conference, I also met with leaders in the health tech industry whom we had deep conversations about how to solve real world problems using Partisia Blockchain’s MPC technology. At the IAS event in Germany, with over 25k in attendance, we were the only blockchain company presenting a Web3 solution.
Kurt Nielsen, our president, put it best in this interview where he speaks about the importance of “growing the pie” in Web3. Meaning that in order for Web3 to succeed, we must find new users, new real world use cases, and new ways to solve real problems using this wonderful technology called the blockchain. Yet, everyone I meet in Web3 conferences is always telling me, “I’ve been in this space for the last x number of years.” It is extremely rare to meet someone who says “I’m new to the blockchain space and interested in learning how this can solve our real world problem”.
Fighting for a share of the same pie
The current Web3 conferences, for the most part, have people who are fighting for the “share of the same pie” it has been fighting for multiple years, so to speak. It’s the entity that has the same players, building the same type of applications for the same group of people year after year. And while you have a few real world industries looking to experiment with blockchain, most, if not all of the Web3 focused events I go to are full of people building the same thing, but packaged just slightly differently. Why is this the case?
And so we see two different themes emerging. Those who are the early adopters, the visionaries and pioneers building Web3 and integrating blockchain technology into real world use cases to solve real problems, and those who are looking for the quick token launch and get rich plan disguised with the pretense of revolutionizing an industry. One has a long and promising future. The other… Well, you can only go so far when everyone is fighting for the same pie..
“Privacy, interoperability, and scalability are fundamental principles that have been pillars of past successful technology innovations and they will be for the Web3 industry as well.”
Partisia Blockchain’s focus has always been about collaboration and solving real world problems. We have founders who understand the challenges of the real world. In the real world, privacy is a fundamental human right, and your private information should not be disclosable to everyone. In the real world, people collaborate and work together to grow the market you are in rather than close off your ecosystem to only those who can pay with your own currency. In the real world, infrastructures are scalable, available to support the world’s population. (Think the internet for example) These fundamental principles play out in real world scenarios and while blockchain provides an incredible value proposition, one of decentralization and trustlessness, it is not a complete solution. Privacy, interoperability, and scalability are fundamental principles that have been pillars of past successful technology innovations and they will be for the Web3 industry as well..
This has been our focus, and the reason why our blockchain architecture is built different. And, as a result, we have quite a number of real world partners working to build things that impact the real world. And we continue to garner interest from people who are looking to solve real problems.
We are committed to growing the pie by bringing the technology to non Web3 industries. Use cases like the humanitarian token system, where we are able to distribute financial aid to those impacted in conflict regions. A donation platform where using blockchain technology, aid can be distributed not only quickly, but also transparently giving the donors full visibility to whom and how their donations made an impact. Tackling counterfeit medication in Africa through a combination of transparent and private supply chain infrastructure. These are samples of real world problems Partisia Blockchain is tackling to solve.
In the Web3 space, we are also focused on adding these fundamental principles that are currently missing to help grow the pie within. Providing DeFi solutions that solve for interoperability, scalability and privacy. Partnering with academia to create a framework for DID that governments can support. Building solutions that enable a real trustless, secure, and interoperable self custody solution that can be built to suit the users individual requirement.
The Web3 industry will undoubtedly continue to survive. Thrive even. But it will also evolve from the current hype cycle to something more mature. As this maturity continues, the need to meet these basic fundamental principles will become more apparent. We also need to work together to grow the pie, rather than fighting for a share in the existing pie. And those who understand and share in this vision will help drive the next generation of Web3 solutions. We hope, through this maturity, we will grow the pie, and perhaps see a new friendly face join the next Web3 conference.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
This is part 3 of a three-part series where we review the three key technology innovations of Partisia Blockchain and compare them with other blockchain technologies. You can read our intro and the performance comparison between various other chains here, or read more about the privacy layer comparison here.
Part 3 reviews the various web3 infrastructure aiming to address the issue around interoperability between different chains, the techniques used as well as pros and cons of various technologies.

Partisia Blockchain is deeply committed to interoperability, aiming to foster trust and collaboration across diverse blockchain networks. Its unique architecture addresses the challenges of cross-chain interactions through a multi-faceted approach, including its innovative “Bring Your Own Coin” (BYOC) concept and advanced bridging solutions.
BYOC allows users to pay gas fees in various liquid coins like Ethereum, BNB, MATIC, USDC, and USDT, rather than requiring a native token. This flexibility enhances convenience and accessibility, eliminating the need for users to acquire a specific token for network interaction. Moreover, BYOC enables developers to open their decentralized applications (dApps) to a wider audience, as users can transact with their preferred cryptocurrency. The stable fee structure, pegged to USD, ensures predictability for projects and users alike, regardless of underlying asset price fluctuations.
Partisia Blockchain’s token bridge is another core innovation. It employs a combined approach of double bookkeeping, staking as collateral, and large-scale MPC-based selection of oracle nodes to form a secure and efficient bridge. This design ensures a 1:1 correspondence between tokens across chains, enhancing security and trust in cross-chain transactions. The token bridge also incorporates a mechanism of frequently expiring epochs and MPC tokens as collateral staking, limiting the accumulation of financial risk.
For securing digital assets, Partisia Blockchain offers MOCCA, a decentralized and fully programmable custody solution. This enables institutions, DAOs, exchanges, and wallet providers to collaborate trustlessly to secure the assets of their users. MOCCA’s smart contracts provide flexibility in defining access controls, voting powers, NFT permissions, and transaction rules, catering to diverse custody requirements.
Partisia Blockchain’s versatility also allows it to function as a second layer for other blockchains. By deploying a zero-knowledge smart contract on Partisia alongside a public contract on the Layer 1 chain, dApps can leverage Partisia’s privacy-preserving capabilities without migrating their entire infrastructure. This approach enables seamless integration of privacy features into existing applications, promoting wider adoption of privacy-preserving technologies.
LayerZero is a messaging protocol designed to facilitate seamless communication and data exchange between blockchains, fostering an “omnichain” vision where all chains are interoperable. This is achieved through a Mesh Network architecture that overcomes the limitations of existing cross-chain solutions.
The innovation lies in facilitating communication between blockchains without the need for costly on-chain nodes or insecure middle chains. This is achieved through a combination of Ultra-Light Nodes (ULNs), blockchain endpoints, decentralized third-party oracles, and relayers. Oracles, such as Chainlink and Band Protocol, fetch transaction data from the block header, while independent relayers verify the transaction proof. This dual verification process ensures the security and validity of the message.
Functioning as a messaging layer, LayerZero enables communication between different blockchains and their smart contracts. The Omnichain Fungible Token (OFT) contract standard enables seamless cross-chain token transfers without asset wrapping or intermediate chains. However, this functionality is tied to the LayerZero ecosystem, which limits the potential reach and interoperability of tokens.
Each application built on LayerZero can configure a security stack consisting of several required and optional decentralized verifier networks (DVNs) to verify its messages. These DVNs can leverage various validation methods, including zk-technology, middlechains, and consortium signers. Additionally, Rate Limiter allows controlling the number of cross-chain messages within a specific time frame, preventing denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and ensuring regulatory compliance. However, this is at a cost of performance.
This flexible approach to security empowers applications built on LayerZero to tailor their verification mechanisms to their specific needs and risk profiles. By not prescribing a single method, LayerZero allows for a diverse range of security configurations across the ecosystem.
Cosmos is designed to be the “Internet of Blockchains,” addressing the limitations of isolated blockchain networks. It achieves interoperability and scalability through a combination of innovative technologies and a modular architecture.
Instead of a single monolithic blockchain, Cosmos allows for the creation of multiple independent blockchains, each with its own specific use case and consensus mechanism. Developers can leverage pre-built modules for common blockchain functionalities, reducing development time and complexity.
The Cosmos Hub serves as the nexus for the entire Cosmos ecosystem. It acts as the intermediary connecting various blockchains within the network. Instead of each blockchain directly linking to every other chain, they all plug into the Cosmos Hub. This hub keeps track of interactions and facilitates communication among different zones (blockchains) in a secure and efficient manner.
Cosmos ensures security through a decentralized validator model. Each chain has its own set of validators responsible for verifying transactions and securing the network. This decentralized approach eliminates single points of failure and enhances the overall security of the ecosystem.
Replicated Security is a feature that allows the Cosmos Hub to provide its strong security to other blockchains, known as “consumer chains” through the IBC protocol. This enables consumer chains to benefit from the Cosmos Hub’s security without needing to maintain their own validator sets.
Interchain Accounts (ICA) represent a significant advancement in cross-chain interoperability, making the Cosmos ecosystem more interconnected and user-friendly. With ICA, applications can directly access and utilize functionalities of applications on other chains and users are able to perform actions like token transfers, swaps, staking, and governance participation from a single account. The benefits of ICA extend to various use cases, including cross-chain liquidity provision, lending, borrowing, and NFT transfers. It enhances governance by allowing voting on proposals across multiple chains without switching accounts.
In addition to IBC, Cosmos supports bridge protocols like Gravity Bridge and Wormhole Gateway. These bridges connect the Cosmos ecosystem with other blockchain networks like Ethereum and Solana, further expanding interoperability and enabling asset transfers and cross-chain communication between diverse ecosystems.
The comparative analysis of various blockchain technologies reveals a spectrum of approaches to privacy, scalability, and interoperability.
Partisia Blockchain’s focus on privacy is not only a technological advancement, but also a philosophical shift towards a more user-centric and privacy-conscious approach to blockchain technology. By seamlessly integrating cutting-edge cryptographic techniques, such as multi-party computation (MPC) and zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs), with a high-performance blockchain architecture, it presents a unique paradigm that transcends the limitations of traditional blockchain models. This fusion of privacy and performance empowers the development of decentralized applications and smart contracts capable of securely processing sensitive data while maintaining scalability and interoperability across diverse networks.
As the demand for privacy-centric applications continues to grow, Partisia Blockchain’s innovative solutions will be instrumental in driving the next wave of decentralized innovation. Its ability to address the inherent challenges of blockchain technology while maintaining efficiency and interoperability positions it as a compelling platform for building the next generation of decentralized applications.
As we kick off the third quarter, July 2024 has been a busy and exciting month for Partisia Blockchain. In this update, we are thrilled to announce the launch of Project RESCUE, new partnerships, and the listing of the $MPC token on Bitpanda. We will also provide a sneak peek into upcoming events like BlockStart in Glasgow. Read on for all the details and stay tuned to our social channels for more updates.
The Partisia Blockchain Foundation proudly announced the launch of Project RESCUE, the world’s first blockchain-based social impact funding initiative that enables end-to-end traceability of donations. This project is both a testament to our commitment to doing good and a demonstration of how blockchain can affect positive change in the world. This marks just the beginning of our implementation of projects launching on Vorne.ai and other initiatives similar to Project RESCUE. Check out our summary of the event here.
July was filled with LOIs and new grant agreements. Starting with Truflation and their push into the RWA space, they agreed to work with Partisia Blockchain to further their existing RWA pricing service, using Partisia Blockchain’s MPC to help privatize certain elements of the assets they are digitizing.
Degen House also signed an agreement to build two potential solutions on Partisia Blockchain: a proof of concept for a payment system similar to the ICRC design but for public use, and an NFT marketplace.
Digital Assets Technologies AG (DAT.AG) received a grant to build the world’s first privacy-preserving, secure environment for transaction and asset verification. It is not just about locking down data; it is about ensuring that data can be shared and verified in a manner that aligns with modern privacy expectations and compliance demands. Essentially, it is a platform for easy audit compliance in the Web3 world.
On 16 July 2024, we were thrilled to announce that the $MPC token was listed on Bitpanda! This listing opens the door for more users to explore the innovative MPC technology, which provides cutting-edge data encryption and unparalleled security on Partisia Blockchain. Dive in and experience the future of secure digital transactions with $MPC.
Kurt Nielsen, Co-Founder of Partisia Blockchain, shares his insights on how Web3 and MPC technology can revolutionize the data economy by empowering users with control over their data. Discover how MPC is paving the way for secure and decentralized collaboration. Read more in Disruptive Tech News: Is Web3 Still Relevant? The Jury’s Still Out, But the Clock Might Be Ticking for This New Paradigm
Join us at BlockStart in Glasgow, Scotland, on 1-2 August 2024. Our Chief of Growth, Shirly Valge, will be sharing valuable insights on the projects we are working on and emerging trends in blockchain. She will be part of engaging panel discussions on “How do global Web3 projects manage local regulations?” and “From physical to fractional: How Tokenization is democratizing access to real-world Assets”. Do not miss the chance to connect with Shirly, you can book your meeting here.
We are excited to share that the final computation of phase 1 of the AirDrop has begun and we are anticipating possible distribution in mid to end of August. Phase 2 will begin soon after tying with the launch of our DEX from zkCross. This marks a significant milestone as we continue to engage with our community and expand the adoption of the $MPC token. Stay tuned for more details on how you can participate and what to expect as we move forward.
As we gear up for Token 2049 in Singapore on 16-21 September 2024, we are thrilled to connect with our community at one of the largest crypto events of the year. Be sure to visit our venue and join us for engaging discussions and insights into the latest from Partisia Blockchain. Stay tuned to our social channels for more updates and details. We look forward to seeing you there!
Bruce Ahn, Chief Success Officer, and Mathias Glintborg, Head of Product, will join X Spaces on 2 August 2024 to discuss adoption, the product roadmap, and other topics. Do not miss this opportunity to get an update on the latest developments and ask your burning questions! Set your reminder here.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
This is part 2 of a three-part series where we review the three key technology innovations of Partisia Blockchain and compare them with other blockchain technologies. You can read more about Partisia Blockchain as well as the performance comparison between various other chains here.
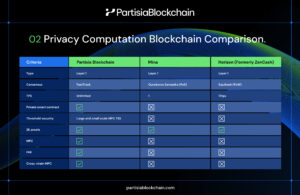
Partisia Blockchain’s core technology, multiparty computation (MPC), allows multiple parties to jointly compute a function on their private inputs without revealing those inputs to each other. This enables secure collaboration and data sharing while preserving confidentiality.
The pursuit of privacy leads to the creation of a groundbreaking zero-knowledge layer. In Partisia Blockchain’s implementation, the input data is secret-shared among multiple nodes, and the computation is performed on these shares, ensuring that no single node can access the raw data.
This ZK layer combines various cryptographic techniques to ensure data confidentiality, integrity and privacy throughout the entire lifecycle of a transaction.
This multi-faceted approach to privacy ensures that user data remains confidential, secure and tamper-proof throughout its lifecycle.
Partisia Blockchain’s MPC smart contracts are designed for comprehensive coordination of both public and private computations. A key differentiator is the introduction of private smart contracts, which streamline the integration of zero-knowledge computation and MPC-as-a-Service solutions.
By integrating Partisia Blockchain’s suite of privacy-centric tools, developers and projects can seamlessly implement best-in-class privacy measures and harness the power of most notably MPC for different use cases.
Mina Protocol is a Layer 1 blockchain that enhances privacy through its utilization of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs). These ZK proofs allow for the verification of transactions and the state of the blockchain without revealing sensitive details publicly. However, it is important to note that while transaction details are obscured on the public ledger, node operators still have access to the actual transaction data.
Notably, Mina’s ledger remains a mere 22KB in size, regardless of the number of transactions, ensuring lightweight accessibility and efficient verification.
At the core of Mina’s consensus mechanism is Ouroboros Samisika, a (PoS) protocol derived from Cardano’s Ouroboros. This protocol enables Mina to resolve long-range forks without relying on transaction history or risking centralization. Ouroboros Samisika utilizes verifiable random functions (VRFs) to select block producers, safeguarding the network against Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks while ensuring scalability.
Leveraging recursive ZKPs allows the creation of an open database of verified statements, fostering composability within the ecosystem. Applications can interact and build upon each other’s verified data without compromising privacy or incurring excessive fees. The “proof of everything” concept allows for the creation of a decentralized network where data and actions are verified and readily usable by other applications, enabling scalable blockchain applications that leverage collaborative computation.
Mina’s forthcoming upgrade aims to further enhance its ZK capabilities, enabling ZK smart contracts (zkApps), Layer 2 solutions, and bridges. This upgrade moves smart contract execution off-chain while maintaining on-chain verification, addressing challenges like data constraints and gas costs.
As for network throughput, many may be confused by the 1 tps, but the developers want to keep the blockchain super lightweight and perform main computations offchain relying on zero-knowledge technology.
Horizen (formerly known as ZenCash) is a privacy-focused Layer 1 blockchain platform that leverages zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) and cross-chain protocol Zendoo empowering developers to create customizable sidechains, each with independent consensus mechanisms, tokenomics and functionalities. This architecture allows dApps to operate on their dedicated sidechains, eliminating bandwidth competition and ensuring optimal performance.
Although Horizen’s mainchain relies on the PoW consensus, its zk-SNARK implementation enhances scalability and throughput. By compressing the data needed for transaction validation, zk-SNARKs enable the mainchain to verify the validity of numerous sidechain transactions within a single block.
In essence, zk-SNARKs act as a certificate of validity for sidechain transactions. The sidechain validates its transactions as usual, then constructs a zk-SNARK proof that summarizes the state of the sidechain. The mainchain nodes verify this proof, confirming the correctness of the sidechain’s transactions without needing to validate each one individually.
The upcoming EON 2.0 upgrade represents a significant step forward for Horizen. This upgrade will migrate the Horizen and EON (EVM-compatible sidechain) to a new, fully compatible EVM chain built on the Substrate framework with tight integration to the zkVerify protocol. This will enable faster and more cost-efficient verification of zk-proofs, further enhancing Horizen’s privacy and scalability capabilities.
Conclusion: Partisia Blockchain stands out alone as the only blockchain enabling a customizable privacy layer to enable computation of private information for providing proofs using MPC or ZKP. While other blockchains use ZK proofs, it is more used for performance and proving of a block rather than computation of actual private data.
The emergence of Web3 and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has ushered in a new era of digital innovation, promising a paradigm shift towards greater transparency, efficiency and accessibility. However, the realization of this necessitates addressing several technical and conceptual challenges inherent in the underlying blockchain technology.
The “blockchain trilemma”, a well-documented conundrum, highlights the intricate trade-offs between decentralization, security and scalability. Achieving an optimal balance between these three pillars is essential for creating a robust, secure and efficient decentralized ecosystem capable of supporting widespread adoption.
This confluence of challenges necessitates the development of sophisticated solutions that can simultaneously address the blockchain trilemma while ensuring robust privacy protection. Partisia Blockchain emerges as a sophisticated response to these challenges through the integration of advanced privacy-preserving cryptographic techniques with a high-performance blockchain architecture.
Partisia Blockchain is a Layer 1 blockchain that redefines the paradigm of decentralized technology by seamlessly integrating privacy-preserving mechanisms with a high-performance architecture. This unique approach addresses the inherent challenges faced by traditional blockchain models, such as scalability limitations and the potential compromise of sensitive data due to the public nature of distributed ledgers.
Central to Partisia Blockchain’s innovation is the implementation of a privacy layer that enables zero-knowledge (ZK) computations to run in parallel with activities on the public blockchain. This groundbreaking integration of blockchain technology and multiparty computation (MPC) vastly expands the possibilities of decentralized applications, allowing for confidential transactions, secure data sharing, and regulatory-compliant solutions.
The platform’s consensus algorithm FastTrack model, a novel approach that combines optimistic block production with a robust Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) mechanism, ensures both rapid transaction validation and the highest levels of security.
Addressing the scalability challenge, Partisia Blockchain employs a comprehensive true sharding solution. This approach dynamically expands the network with manageable segments (blockchains), allowing for efficient processing of high transaction volumes without compromising consensus or security.
To foster a more interconnected blockchain ecosystem, the network has implemented a native collateral bridge, facilitating the secure transfer of assets and information between the Partisia Blockchain and other networks, promoting interoperability and collaboration.
The commitment to privacy extends to the MPC-as-a-Service platform, providing developers with a comprehensive suite of tools. This platform streamlines the orchestration of privacy-preserving computations, enabling a wide range of use cases, from confidential financial transactions to private auctions and secure data sharing.
Finally, Partisia Blockchain fosters a thriving and reliable network through a market for trust that incentivizes node operators to validate transactions, propagate information and provide MPC-as-a-Service. This mechanism ensures that the network is supported by transparent and efficient nodes; thereby, maintaining the highest standards of security and performance.
In this three-part series, we will dive deeper into performance, zero-knowledge technology, and the cross-chain messaging technology stack of Partisia Blockchain versus other solutions in the field.
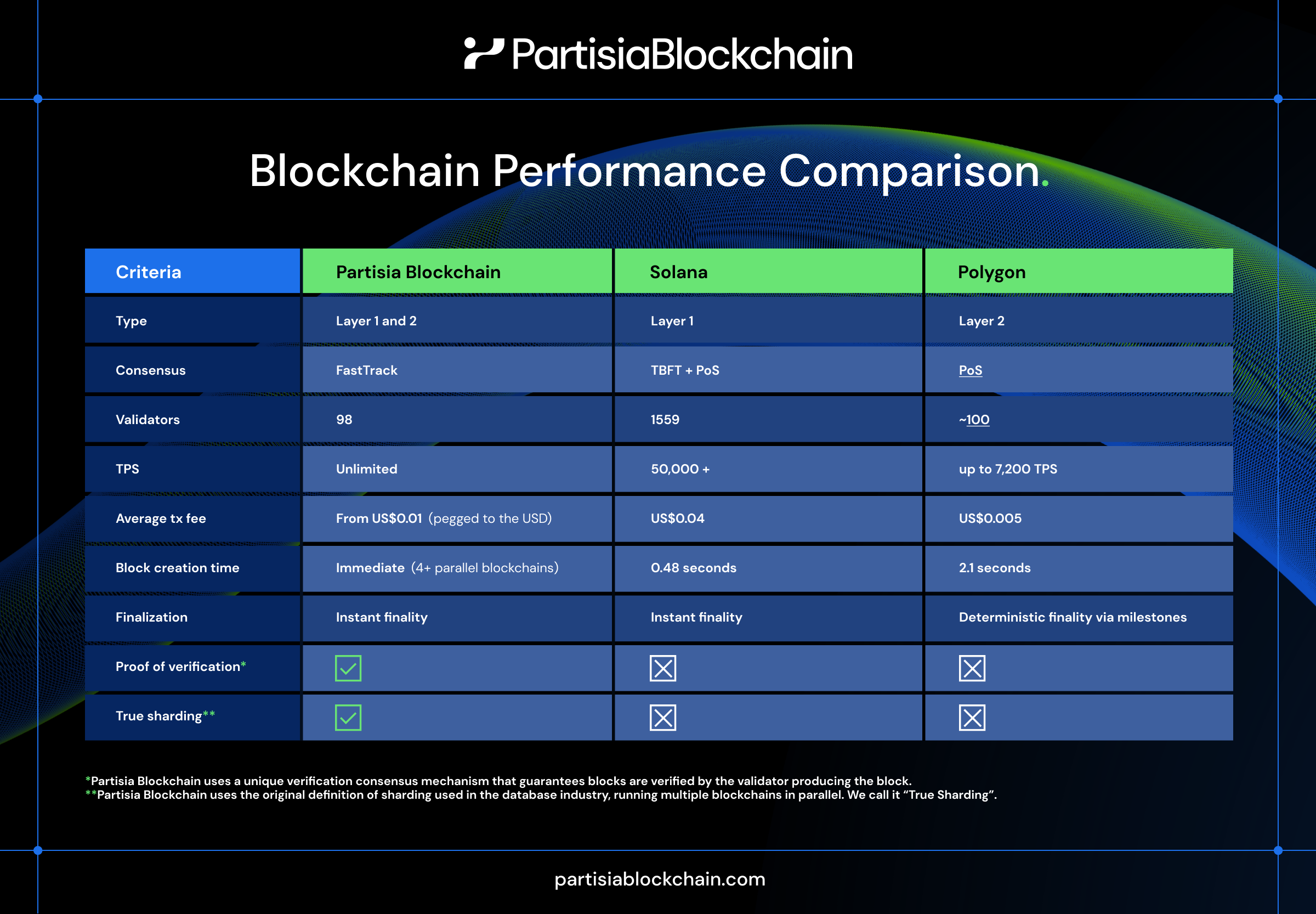
*Partisia Blockchain uses a unique verification consensus mechanism that guarantees blocks are verified by the validator producing the block.
**Partisia Blockchain uses the original definition of sharding used in the database industry, running multiple blockchains in parallel. We call it “True Sharding”.
Partisia Blockchain stands as a robust and adaptable Layer 1 blockchain that prioritizes privacy, scalability and decentralization. Its innovative FastTrack consensus mechanism, incorporating Proof of Justification (PoJ) and Proof of Finalization (PoF), ensures robust security and transaction finality. The Proof-of-Verification (PoV) mechanism further enhances security by guaranteeing that validators personally verified each block.
The scalability challenge is tackled through a dynamic sharding approach. Unlike traditional blockchain sharding, in Partisia Blockchain shards are an independent blockchain that can separately create, verify and validate a block. While most blockchains create one block at a time, Partisia Blockchain leverages its sharded architecture, now it is four shards (four chains), to generate four blocks at a time and there is no limit.
This architecture allows for true parallel blockchain processing. In the event of congestion, the system can dynamically create new shards, adding capacity on the fly. This dynamic scalability architecture theoretically enables the network to scale horizontally infinitely.
The platform’s versatility is further amplified by its support for diverse node types, each with specialized functions. These include reader nodes for accessing information, baker nodes for producing and validating blocks, ZK nodes for zero-knowledge computations and oracle nodes for oracle services. This diversity caters to a wide array of use cases, making Partisia Blockchain adaptable to evolving demands.
It is also important to mention that Partisia Blockchain eliminates the volatility and unpredictability often associated with blockchain transaction fees. This differs from traditional blockchain models with an approach that combines a fixed-fee structure tied to the US dollar, offering users stability and convenience. This means users know exactly how much they will pay for a transaction, making cost estimation straightforward and budgeting easier.
Furthermore, Partisia Blockchain offers flexibility in fee payments by not limiting them to the native $MPC token. Users can choose to pay network fees using other supported tokens, enhancing convenience and accessibility.
This feature we will explore further in this article.
Solana achieves high speed and scalability through its Proof of History (PoH) timekeeping mechanism, combined with Proof of Stake (PoS) and Tower BFT for consensus. Its Sealevel parallel smart contract execution and Turbine block propagation further enhance its performance.
Solana’s software is designed to get out of the way and let the hardware operate at capacity, while most blockchain systems need to work on optimizing the software to improve their throughput. As such, Solana scales naturally with bandwidth, SSDs, and GPU cores. It is a good solution, but resource-intensive and expensive for node operators.
The fee structure consists of a base fee per transaction and priority fee that allows users to expedite transactions by paying more during high network congestion. This fee is calculated dynamically, based on current demand and desired confirmation time. Solana also has a “rent” fee, a withheld balance in each account to cover on-chain data storage costs.
Polygon distinguishes itself by offering a multi-layered approach to scaling Ethereum. Its PoS sidechain provides a parallel network for faster and cheaper transactions while still maintaining compatibility with Ethereum. The Polygon zkEVM leverages zero-knowledge rollups to bundle and verify transactions off-chain, further increasing scalability and reducing costs.
With the Polygon 2.0 (zkEVM validium) update, the network is set to become a network of ZK rollup chains, enabling interoperability and a wider range of applications while maintaining the security of the Ethereum mainnet.
While offering significant scalability advantages over Ethereum, Polygon has challenges with transaction finality due to its reliance on checkpoints on the Ethereum mainchain. In its PoS chain, transaction finality is not immediate. It requires a waiting period before the transaction is considered final after a checkpoint sent to Ethereum. This process is slow and introduces the risk of deep chain reorganizations, affecting the overall user experience.
To address this, Polygon implemented the “Deterministic Finality via Milestones”. Milestones, similar to Ethereum’s checkpoints, signal the finality of blocks in the validator layer allowing to achieve faster finality, minimizing the risk of following an incorrect chain for an extended period. While the milestones solution addresses the finality issue, Polygon’s PoS inherently comes with certain limitations regarding throughput. The number of validators in the network is limited, which can potentially bottleneck the transaction processing capacity. Moreover, while zkRollups offer scalability advantages, they also have their own throughput limitations due to the computational requirements of generating zero-knowledge proofs.
Speaking about fees, Polygon offers lower transaction fees than Ethereum. The fees on Polygon PoS, consist of a base fee and a priority fee to speed up processing, both paid in $MATIC. The base fee, which fluctuates depending on network congestion, is then burned. Polygon zkEVM, based on zero-knowledge rollups, also incurs gas fees paid in $MATIC to cover computational costs.
Stay tuned for Part 2 of the series where we will delve deeper into the zero-knowledge technologies and compare Partisia Blockchain with other blockchains.
ZUG, 9 JULY 2024. Partisia Blockchain grants the Digital Assets Technologies (DAT) AG. to launch a platform designed to tackle critical data security and privacy issues. Tailored for auditors and blockchain organizations, the DAT’s platform will be a robust mechanism for proving asset ownership while ensuring privacy and compliance.
Traditional data transmission methods are increasingly inadequate, often leading to security breaches and undermining transaction integrity. This vulnerability affects not only auditors and blockchain organizations but also poses significant risks to Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs), banks and end consumers. The Partisia Blockchain-supported DAT solution will address these challenges by offering a secure, privacy-preserving environment for transaction and asset verification.
The Partisia Blockchain-backed DAT platform will be designed to balance the need for transparent audits with the right to privacy in digital transactions. This approach ensures data can be shared and verified in a manner that meets modern privacy expectations and compliance regulations, making it essential for financial institutions and end-users.
The DAT solution will combine advanced technology with industry expertise to deliver features tailored for blockchain entities and financial auditors:
The Partisia Blockchain-supported offering’s security architecture prioritizes privacy and security without sacrificing usability, featuring:
The DAT’s solution will uphold strict standards, aligning with ISO 27001 and SOC 2 frameworks to deliver a robust compliance posture. This suite of features ensures that the offering meets today’s market and regulatory requirements and can adapt and scale to future demands.
About Partisia Blockchain: Partisia Blockchain brings unparalleled opportunities by empowering privacy-preserving, interoperable and sustainable innovation for fairness and transparency. It fuels the most secure and efficient networks to solve global problems. Distilled with 35 years of rigorous research, Partisia Blockchain future-proofs solutions, solves tomorrow’s challenges by powering fair, secure, distribution of benefits. While preserving privacy and confidentiality, it brings accountable, transparent and decentralized governance. Learn more: www.PartisiaBlockchain.com
About Digital Assets Technologies (DAT) AG.: Digital Assets Technologies (DAT) AG offers secure, privacy-focused SaaS solutions for CPAs, financial auditors and digital asset companies. Created by seasoned blockchain experts, the platform revolutionizes accounting, financial audits and travel rule compliance with top-tier security and regulatory adherence. Learn more: https://dat.ag
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
June marked a successful close to Q2 for Partisia Blockchain, filled with strategic collaborations, exciting platform launches and insightful community interactions. Highlights include HIEx’s Vorne platform launch, our successful AirDrop Program and the release of our comprehensive DeFi guide. Stay tuned as we recap key events, share our latest innovations and look ahead to impactful partnerships and initiatives in July.
This month, our highlight was the launch of HIEx’s Vorne.ai platform. The world’s first blockchain-based social impact funding platform launched with fanfare during the 77th World Health Assembly in Geneva. The platform aims to address one of the main drawbacks of donations which is the reporting of what your donation actually impacted. Look for the platform being highlighted in the 25th IAS conference in Munich in July! We also announced the launch of StakingRewards.com, a platform that lists many of the top tier networks and their staking rewards. Go check out their website to see how we compare to other chains and stake.
zkCross Network, our DeFi partner, also launched their on-ramp platform, enabling more than fiat currencies to be able to purchase Partisia Blockchain’s BYOC tokens. In the future, look for the integration to enable people to be able to buy MPC tokens directly using a credit card, Google Pay and Apple Wallet. Month of June was full of launches, with CV Pad supporting Partisia Blockchain and helping to fund teams building on top of our chain. Alongside CV Pads, we also announced Moonrig’s grant to build the world’s first crypto asset analytics platform, with accredited research analysts reviewing the various crypto assets in a more structured and professional way.
The first tranche of Partisia Blockchain’s highly anticipated 25 million MPC token AirDrop Program has ended. We are pleased to see the heightened interest in the Partisia Blockchain AirDrop Program. The next tranche—already in the works—will help power our DeFi suite of solutions. Participants, who keep their tokens bridged on Partisia Blockchain, will benefit from an early qualifying criteria for the second tranche of the 25 million MPC token AirDrop Program. During the second tranche, planned for 2024, dApps and projects scaling DeFi solutions will be deployed on mainnet and expand the scope of new use cases.
Our Chief of Growth, Shirly Valge, led an insightful workshop at the Crypto Valley Conference in Zug, Switzerland, on 6 June 2024, captivating the audience with her expertise. In her session, “Integrating Privacy and Compliance,” she delved into the innovative solutions Partisia Blockchain is developing including how we are pioneering privacy-enhancing technologies while ensuring regulatory compliance. We extend our gratitude to the Crypto Valley Conference for having us and look forward to future collaborations.
Our Head of Product, Mathias Glintborg, recently joined an enlightening podcast episode hosted by Concordium in collaboration with Novo Nordisk. This discussion delves into the intricacies of blockchain product development, offering valuable insights from industry leaders. It’s a must-listen for anyone interested in the future of blockchain. Catch up here. Meanwhile, Chief Product Officer, Mark Bundgaard, joined Anca Petre for an engaging conversation on the transformative impact of Partisia Blockchain in the healthcare sector. In this episode, Mark explores our Layer 1 blockchain architecture, explains the nuances of multiparty computation (MPC), and highlights what makes us stand out in the blockchain world. Listen here.
Our first Zealy competition has been a tremendous success. In June, we were thrilled to share the winners, and we extend our heartfelt thanks to everyone who participated and supported our project. We saw an impressive 5,029 Zealy members sign up, with a total of 30,489 quest claims completed. A total of 50,000 $MPC tokens in rewards were distributed to our community. Read the full announcement on our Discord.
The Q8 rewards for our stakers were released in June, distributing one of our largest rewards yet—over 2.7 million $MPC tokens to more than 1300 wallet addresses. Don’t miss out on a 53% APR; stake your tokens today.
Understanding blockchain does not have to be difficult. That is why we have created a series of videos that explain Partisia Blockchain in a fun and engaging way for everyone, from kids to Web3 experts. Watch the first 3 levels presented by Maria Cocu, Bakyt Azimkanov, and Bruce Ahn. Stay tuned on our socials for more!
Our new DeFi guide is now live. This detailed walkthrough provides a deep dive into low-level interfaces of decentralized finance, covering everything from interacting with smart contracts to building scalable decentralized exchanges (DEXes) using our Scalable Automated Market Maker (AMM) framework. We encourage development teams to leverage this guide to create user-friendly DeFi applications on top of these foundational contracts. Whether you’re a seasoned blockchain developer or just starting out, our guide offers the essential tools and knowledge to succeed in the dynamic world of decentralized finance.
The community is at the heart of every Web3 project, and the same goes for Partisia Blockchain. On 26 June 2024, we hosted a Twitter Spaces event to answer the community’s most pressing questions. Co-Founders Peter Frandersen, Kurt Nielsen and Brian Gallagher participated, discussing upcoming plans, our new DeFi strategy, RWA and AI, as well as the dealflow of new projects (spoiler alert: we are seeing significant growth!). Here is the recorded Twitter Spaces session.
On 22-24 July 2024, Partisia Blockchain will attend the 25th annual International AIDS Society event in Munich, working with notable organizations, such as Social Equation Hub, GNP+ and the Elton John Foundation to help raise funds to combat the HIV virus. The platform that will support the event will be none other than Vorne.ai. See you in Bavaria!
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Missed our live Twitter Spaces with the Partisia Blockchain Co-Founders? Fear not, here is the recap of one of our most awaited AMA sessions with Peter Frandsen, Brian Gallagher and Kurt Nielsen.
Kurt: We are focusing on DeFi and Real-World Assets (RWA) with a touch of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The Web3 space needs to grow beyond its current user base. This requires expanding into new areas and addressing regulations and compliance, which Partisia Blockchain is well-equipped to handle.
Peter: We are moving from technology development to building solutions by creating standards and templates for DID, NFT and RWA, making it easier to develop products on our platform.
Brian: We have been working on Parti.com, a SocialFi platform that combines decentralized finance with a creator platform, eliminating the middleman. Users get a Partisia Blockchain wallet for identification.
1. What new marketing strategies are you considering implementing? How do you evaluate the effectiveness of your current strategies on the token price and the onboarding of new applications?
Brian: We are shifting our focus from technology development to product marketing, particularly in DeFi and RWA. We are also expanding our presence in the Asian market. Collaborating with high-profile key opinion leaders (KOLs) on platforms, like Telegram and YouTube, has been key. Over 60 Tier 1 KOLs and more than 200 lower-tier KOLs have helped distribute and create content about Partisia Blockchain. Our follower count has grown by nearly 30,000 (13%), Medium subscribers by almost 150% and our Discord community by nearly 130%.
2. How do you plan to attract new projects to increase utility? What are your thoughts on the potential benefits and drawbacks of attracting projects with varying levels of interest?
Kurt: We aim at high-quality projects and work with them to ensure proper adoption. Our mainnet supports all types of Web3 projects, focusing on DeFi and RWA. We are also working on high-profile projects in advertising, gaming, AI and confidential data management. Since January 2024, we have launched six projects on mainnet, have 20 projects in development, and added more than 300 leads to our funnel.
3. In what ways do meetings in locations, such as Ibiza and Split, contribute to securing partnerships and project signings?
Kurt: Conferences and industry meetings are crucial for securing partnerships. The TEAMZ and Nordic Blockchain Conferences allowed us to discuss our strategic direction in RWA and DID. The WHA and HIEx events exposed new audiences to blockchain’s value. Token2049 brought in many new leads.
4. How can you provide more precise details about your plans to reassure the community about Partisia Blockchain’s future?
Kurt: We are building the most advanced blockchain infrastructure. Our smart contract templates address issues like front-running while complying with regulations such as MiCA.
5. Can you explain the process and considerations behind the communication of the listings? How do you plan to keep the community better informed in the future?
Brian: Compliance considerations are crucial for exchange listings. We have communicated launch days in a compliant manner and plan more AMAs and interviews.
6. What information can you provide about the timeline for the conclusion of the AirDrop?
Peter: The first part of the AirDrop has ended, and we are moving to the claiming phase. Exact dates for the next phase are not available yet, as I am not doing it all by myself.
7. How does the roadmap support DeFi?
Kurt: A new landing page will soon present our DeFi package, including on-chain custody (MOCCA), DID solutions and an AMM solution.
8. Do you have any plans on improving access to information about upcoming AirDrops, such as providing a calendar or adding a referral system?
Peter: We will improve communication around AirDrops, utilizing more AirDrop sites and ensuring information is relayed to the community.
9. Is Partisia Blockchain planning on increasing media engagement through influencer videos on platforms, like YouTube, or is the team using other methods?
Brian: Yes, we plan to increase media engagement through influencer videos on platforms like YouTube.
10. How do you assess the market performance of the token since its launch? What reflections do you have on the initial public sale pricing of 40¢?
Brian: Our token is a utility token for running nodes. We cannot comment on prices of tokens, but I can say that we focus on its use and adoption in DeFi.
11. What are the most significant challenges Partisia Blockchain faces in onboarding new dApps?
Kurt: We can only talk about some projects, and we update regularly wherever we can. But at a high level, we have an extensive pipeline built and feel that the adoption is moving in the right direction.
12. What do you think about the team’s pivot towards new product-market fits, such as Real-World Assets (RWA) and artificial intelligence (AI)?
Kurt: We are focusing on AI by creating transparency in data used for training models and ensuring confidential use of this data. Additionally, we are integrating AI with Decentralized Identification (DID) to keep user preferences hidden while allowing AI to make decisions on their behalf.
13. How is Partisia Blockchain bringing United Nations’ SDG goals to life?
Peter: Partisia Blockchain is actively working on multiple projects, including a solution for the International Committee of the Red Cross and the implementation of eIDAS, the European standard for DID. Further details will be announced as these initiatives progress.
A recording of this session is available on Partisia Blockchain’s official X (Twitter) account. A special thank you to the community members that provided us with these questions. We look forward to answering the rest of them in our upcoming AMAs.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
This is a demonstration of how to get started with DeFi on Partisia Blockchain focusing on interacting with smart contracts directly via blockchain explorer on TestNet and building DEXes based on the Scalable AMM framework developed by co-founder, Kurt Nielsen. There’s currently teams building out DeFi on Partisia Blockchain for MainNet – one example is zkCross Network.
This new AMM DEX design is intended for builders to reinvent traditional finance with a more fair and compliant DEX that ensures scalability, price guarantee, and frontrun protection – all features you will not find in a regular DEX model out-of-the-box. Note that this guide is a walkthrough of a low-level interface to learn the mechanics, and we are encouraging teams to take this and build a user-friendly DeFi app on top of these contracts. Is your team ready to build the next frontier of finance? Read more about our Grants Program.
First things first, let’s meet the testnet tokens and smart contract that we will be using in this guide.
Now, go to Partisia Blockchain’s Discord server and open a #support-ticket. Choose Developer Support option, and indicate you need test gas and IWH tokens. If you don’t have a wallet already, you can use Parti Wallet. Note: to show your MPC20 tokens in Parti Wallet, go to the “MPC20” tab and then “Manage Tokens”.
Here we use the DEX router for swapping across multiple pairs and liquidity pools to demonstrate the lock-swap price guarantee concept that can be used for building scalable DeFi that operates cross-chain and on multiple shards. In this case we will swap IWH to PPE.
1. Go IvanWifHat (IWH) token contract and sign in with your wallet.
2. Select “Approve” under the “INTERACT” dropdown.
3. Insert the smart contract address of DEX router in “Spender”, select the amount you want to swap (e.g. 50000), and hit “APPROVE” to sign the transaction via your wallet.
Remember IWH has 4 decimals e.g. if you want to approve 5 IWH, insert 50000 in “Amount”. In this guide we use 50000 in “Amount”.
Approval is needed before the DEX router can manage your tokens for the swap.
4. Now go to DEX router and select “Route swap” from the “INTERACT” dropdown.
5. Insert the smart contract address from IvanWifHat (IWH) in the “Token in” field and the smart contract address of PeterPepe (PPE) in “Token out”. Insert the amount you want to swap in “Amount in” e.g. 50000, and the minimum amount you are willing to receive from the swap in “Amount out minimum” e.g. 40000. Click “ADD ADDRESS” twice under “Swap route” and insert the smart contract addresses of QTK/IWH liquidity pool and PPE/QTK liquidity pool in respective order. This will define the route of your swap through liquidity pools. Adjust the gas fee to 500000 and hit “ROUTE SWAP”.
When you set the “Amount out minimum”, take into consideration that each liquidity pool takes a 3% swap fee, gas fees and slippage. In this example we use 50000 “Amount in” and 40000 “Amount out minimum”.
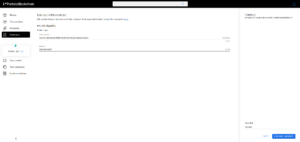
6. Examine the transaction hash to explore routing and the lock-swap price guarantee concept, and check the assets in your wallet.
Now, if you hold two tokens that correspond to a pair in a liquidity pool, you can become a liquidity provider (LP) to earn revenue from the fees paid by other users that swap.
First, make sure you have swapped your way to hold either QTK and IWH or PPE and QTK. In the below example we use QTK/IWH. See above section “Swap via router” for instructions.
1. Go to IvanWifHat (IWH) and approve the smart contract address of QTK/IWH liquidity pool to spend the amount of that token you want to supply as liquidity. Do the same for QuantumKurt (QTK).
Again, remember that IWH, QTK and PPE has 4 decimals.
2. Then go to QTK/IWH liquidity pool and select “Deposit” under “INTERACT”. Now insert the smart contract address of IvanWifHat (IWH), specify the amount, and hit “DEPOSIT”. Do the same for QuantumKurt (QTK).

3. Next, go to the QTK/IWH liquidity pool and select “Provide liquidity” under “INTERACT”. Then insert the smart contract address of IvanWifHat (IWH), specify the amount, and hit “PROVIDE LIQUIDITY”. Do the same for QuantumKurt (QTK).
4. Go QTK/IWH liquidity pool and examine the smart contract state to see your LP.
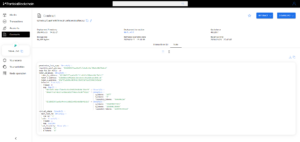
5. If you want to reclaim your liquidity and transfer the tokens back to your account, then use the “Reclaim liquidity” and “Withdraw” function.
You can find all DeFi smart contract templates here if you are interested in deploying your own DEX and explore all functionalities as operator. For more information on how to compile, deploy and interact with smart contracts, please visit the smart contract documentation. Connect with us on Discord for our tech Q&A and apply for our Grants Program if you are interested in building DeFi on mainnet.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
In the last week of May, the global healthcare community convened in Geneva for the 77th annual World Health Assembly of the World Health Organization. This significant event brought together corporate leaders, including pharmaceutical giants, insurance groups and hospital conglomerates, alongside government delegations from around the world. The assembly aimed to address pressing global health issues and explore innovative solutions.
A standout feature of our presence in Geneva was the active participation of Partisia Blockchain and its partner, the UNAIDS spin-off Health Innovation Exchange (HIEx). HIEx organized a series of high-profile events that tackled critical healthcare topics. Attendees included senior executives from Fortune 500 companies, healthcare professionals, fund managers, major foundations, technological innovators, donors, and high-ranking government officials, including ministers, vice ministers and ambassadors from multiple countries.
On 29 May 2024, Partisia Blockchain and HIEx marked a momentous occasion by unveiling a groundbreaking solution during a joint session. HIEx introduced a new platform, Vorne.ai, powered by Partisia Blockchain. This platform built on our technology addresses a significant challenge in healthcare fundraising: the lack of transparency regarding the impact of donations.
Vorne.ai revolutionizes the donation process by providing a simple one-click donation feature coupled with transparent value-chain reporting throughout the lifecycle of donated funds. This innovation allows donors to see the direct impact their contributions are making, enhancing trust and accountability.
Partisia Blockchain plays a pivotal role in this process by facilitating a one-to-one matching of donations with a stable token that is minted, used and tracked to ensure the traceability of each donation’s impact on supported causes. This cutting-edge technology was showcased to global delegations, demonstrating the transformative potential of blockchain and multiparty computation (MPC) technologies.
Our MPC technology is transforming healthcare, research and supply chains. This technology further enhances the capabilities of blockchain, offering new dimensions of security and privacy that are crucial for the healthcare sector. Here is how MPC is transforming various sectors:
Healthcare data privacy: MPC allows multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private. This is particularly valuable in healthcare, where patient data privacy is paramount. MPC enables secure data analysis and sharing among healthcare providers without compromising patient confidentiality, leading to better diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
Collaborative research: In the research sector, MPC facilitates secure collaboration between institutions. Researchers can share and analyze sensitive data without exposing it to unauthorized parties. This accelerates the pace of medical discoveries while maintaining data privacy and security.
Pharmaceutical industry: MPC technology ensures secure sharing of proprietary data among pharmaceutical companies during medicine development. It enables collaborative research and development while protecting intellectual property, thus fostering innovation, reducing inefficiencies and accelerating the creation of new therapies.
Medical supply chain management: MPC enhances supply chain transparency and security. By ensuring that sensitive information, such as components, pricing and supplier details, is protected, MPC allows stakeholders to verify the authenticity and quality of medical supplies without exposing confidential data. This leads to a more reliable and efficient supply chain.
Partisia Blockchain is proud to partner with HIEx in this groundbreaking initiative. Through this collaboration, we are making significant strides in realizing the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Vorne.ai represents a critical first step in creating innovative solutions that address real-world issues in both the public and private sectors.
The 77th World Health Assembly highlighted the critical role of innovative technologies like blockchain in addressing global healthcare challenges. The unveiling of Vorne.ai by HIEx and Partisia Blockchain showcases the transformative potential of blockchain in creating transparent, efficient and impactful solutions for the healthcare sector. As we continue to advance these technologies, our commitment to supporting the UN SDGs remains unwavering. Through strategic partnerships and continuous innovation, we aim to transform the healthcare landscape, solving some of the world’s most pressing healthcare problems and making a tangible impact on global health and well-being.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
GENEVA, 11 JUNE 2024. Partisia Blockchain announces the launch of Vorne.ai, an innovative fundraising platform developed by the Health Innovation Exchange (HIEx) and powered by Partisia Blockchain and its multiparty computation (MPC) technology. This pioneering platform is set to transform the landscape of healthcare fundraising by addressing a critical issue: the lack of transparency in demonstrating the impact of donations.
Health Innovation Exchange is dedicated to improving access to healthcare worldwide. With the introduction of Vorne.ai, HIEx tackles the longstanding challenge of transparency in fundraising. For the first time, Vorne.ai offers not only a simple one-click donation feature, but also transparent value-chain reporting throughout the lifecycle of donated funds. This transformative approach ensures that donors can see the direct impact of their contributions, fostering trust and accountability.
Partisia Blockchain plays a pivotal role in this process by creating a one-to-one match between donations and a stable token. This token is minted, utilized and meticulously tracked to ensure full transparency of the impact each donation makes on the supported cause. By leveraging its technology, Partisia Blockchain ensures that every transaction is secure, transparent and immutable, setting a new standard in the healthcare fundraising sector.
Peter Frandsen, Chief Technology Officer at Partisia Blockchain, says:
“We are honored to partner with the Health Innovation Exchange. Through this collaboration, which commenced in Davos during the World Economic Forum, we reaffirm our commitment to advancing the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Our technology not only enhances transparency and accountability in healthcare donations, but also drives significant progress towards achieving the SDGs.”
Enhanced transparency and accountability: Partisia Blockchain’s immutable and transparent nature ensures that all transactions and data are verifiable and secure. Vorne.ai leverages this capability to provide real-time, transparent reporting of fund utilization, thereby increasing donor trust and accountability.
Secure and efficient data management: Partisia Blockchain offers a robust framework for managing and sharing sensitive healthcare data. This ensures that information remains confidential and tamper-proof, leading to improved patient outcomes and streamlined operations.
Improved supply chain management: By providing end-to-end visibility, blockchain ensures that medical supplies are authentic and have been stored and transported under the right conditions. This reduces the risk of counterfeit drugs and enhances patient safety, which plagues many countries in the developing world.
Facilitating interoperability: Partisia Blockchain can serve as a universal protocol for information exchange, enabling seamless access and sharing of critical data across various healthcare platforms and systems.
The launch of Vorne.ai underscores our commitment to bringing the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to life. Specifically:
SDG 3: Good health and well-being: Partisia Blockchain and MPC enhance the efficiency and transparency of healthcare systems, ensuring that resources are used effectively to improve health outcomes.
SDG 9: Industry, innovation and infrastructure: By integrating advanced technologies like blockchain and MPC, we build resilient healthcare infrastructures that support sustainable industrialization and foster innovation.
SDG 17: Partnerships for the goals: Collaborative efforts between entities like Partisia Blockchain and HIEx exemplify the power of partnerships in achieving the SDGs.
This endeavor once again emphasizes the transformative impact of Partisia Blockchain and multiparty computation technology on the healthcare industry and steps being made towards bringing the UN Sustainable Development Goals to life.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
The last month of spring was busy as the plans for the second half of the year started taking shape. Team members convened in Aarhus for a strategic workshop. In-person gathering in Central Jutland took the pulse of the current progress to date against the roadmap, outlined the plans for expanding our service offerings with key focuses on DeFi and RWA (real world assets) solutions. Stay tuned for exciting new developments and be the first to know.
The Partisia Blockchain team enjoyed several days of networking and collaboration at the 77th World Health Assembly in Geneva. Our community learned more about our innovative solutions for healthcare access, discussing how Partisia Blockchain is advancing SDG3 and supporting this year’s theme, “All for Health, Health for All.”
Co-Founder Peter Frandsen demonstrated the impact of Partisia Blockchain in bringing the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to life during his keynote on leveraging blockchain for healthcare access. He also engaged with local press, addressing questions on the intersection of blockchain, innovation, and healthcare, highlighting how Partisia Blockchain is driving transformative solutions in the healthcare sector.
Bruce Ahn, Chief Success Officer, moderated an insightful panel on blockchain’s role in healthcare, wellness, and social impact at WHA77. The discussion highlighted innovative solutions and their potential to transform global health.
The Partisia Blockchain team recently made a significant impact at BlockSplit in Croatia. Our dynamic duo, Shirly Valge and Maria Cocu, were present to share the exciting developments on our horizon. The event provided an invaluable opportunity for days of networking with Web3 startups, developers, researchers, investors, designers, and other innovators from around the globe.
Our Chief of Growth, Shirly Valge, captivated the audience with a powerful keynote on why privacy is needed in Web3 in the growing trend of GDPR and data protection. Her inspiring insights shed light on the crucial role of privacy in the evolving landscape of blockchain technology.
Last but not least, the team was in Warsaw to attend the Next Block Expo, where Shirly took stage to highlight the privacy, interoperability and scalability of blockchains to future-proof the industry. The team also met with our Polish node operators, community members and discussed future ventures with potential partners.
Mark your calendars for 6-7 June 2024. Our Chief of Growth, Shirly Valge, will be at the prestigious Crypto Valley Conference. On Thursday 6 June at 14:00, Shirly will host an insightful workshop focused on integrating privacy and compliance in the blockchain space. This session promises to be a must-attend event for anyone interested in the intersection of privacy, compliance, and innovative blockchain solutions. Stay tuned for more details on our social media.
Partisia Pulse is back! Kurt Nielsen, President of Partisia Blockchain, is featured in the latest edition of this series. Following the launch of the $MPC token, the community has been eager to know what is next. And he was crystal clear: expanding the ecosystem with DeFi and RWA-oriented projects is the target for the rest of the year. “There is more work being done in the background, but these two will be the focus for 2024,” says Kurt in the video. Watch the latest episode here.
Monadi launched their initial testnet version with their mainnet coming in June. Monadi helps companies stay compliant with CSRD regulations by using multiparty computation to compute on company executives’ salaries by gender to ensure they are fair without exposing their individual salaries. Come check them out here.
IDSign received a grant to be the first team to onboard MOCCA (MPC On-Chain Custody Advanced solution) as a solution to protect and provide a customizable custody solution to encrypted documents. MOCCA is not just a custody solution for crypto assets, but all types of digital asset and IDSign is showing the world you can have a decentralized solution for all types of custody challenges.
We were thrilled to see remarkable growth in our AirDrop program throughout May. The community’s participation and enthusiasm have been incredible. Make sure to check out the leaderboard to see where you stand and keep bridging your EVM tokens through the zkCross bridge to climb higher. Exciting rewards await those who stay active and engaged.
Another $MPC rewards quarter is coming to a close. We will distribute more reward tokens to our stakers in June, our largest to date. $MPC2.7 million tokens will be distributed to our stakers who are putting their token to work by securing the network. Learn how your tokens are put to work to secure the world’s data with this quick video.
zkCrossDEX will be launching phase 2 of their project. Their on-ramp system supporting more than 200 fiat currencies alongside their DEX supporting BYOC and MPC20 tokens will be launching mid to end of June. Look for new MPC20 tokens to begin appearing on the DEX soon after the launch.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
by Jesper Buus Nielsen, Chief Cryptographic System Designer
This brief post explains why I believe secure multiparty computation (MPC) is a key technology for creating a better version of the internet and why we founded Partisia Blockchain to unlock its potential.
First, a bit about myself: I am a professor of computer science at Aarhus University in Denmark. For me, MPC and blockchain represent a professional life journey. My PhD thesis in 2003 focused on cryptographic consensus protocols, threshold signature schemes and MPC. Twenty-one years later, these technologies are starting to flourish. Today, they are often known as blockchains, distributed wallets and, well, MPC, and I am still researching them.
If you are reading this post, you probably already know what MPC is. If not, MPC allows multiple servers–each holding private data–to perform computations on the joint dataset without exposing any private data and without revealing anything beyond the computed output. It may sound like magic, but it is just cryptography. For details, see our book here.
I believe MPC has the potential to solve many of the current problems with the internet. The internet was initially envisioned as a space for sharing public information. Instead, it has become a space where we often pour private information into informational black holes, which monetize it in opaque ways, from programmed outrage to influencing voting behavior. You might argue that people should simply stop trading their privacy for trivial rewards. However, when faced with a choice between functionality and privacy, people tend to choose functionality. It is unrealistic to expect this to change, as humans are short-sighted utility optimizers. Fortunately, there is no need to choose between functionality and privacy. MPC demonstrates that you can eat your cake and have it too.
We just need to integrate MPC into everything. Imagine a dream world where using MPC is easy and free. If you wanted to compute on a dataset from several sources, you would simply specify the desired computation in your favorite programming language, indicate where the data is located, compile the code, deploy it, run it. And voilà, the desired result would magically appear where it should, with no leaks. And this process would be as efficient as computing the result on a single computer. Moreover, it would be completely transparent, allowing you to know and control exactly how and when your data was used. Had the internet looked like this from the beginning the way we store and process private data would be completely different, and thousands of new applications would be possible. This does not have to remain a dream world. We can build it, and we should build it!
Two decades ago, I thought researching better MPC protocols would be enough for the world to adopt them. However, implementing and deploying MPC turned out to be more challenging than I anticipated. In 2008, I co-founded Partisia ApS to put MPC into practice. This experience taught me a lot about the real-world challenges of using MPC. For each new use case, we often had to design a new optimized protocol, implement it, and find servers to run it. The hardest part was finding mutually trusted, organizationally separate parties to run the servers and teaching them how to use MPC. While there is still a place for such deployments, it became clear that this approach would not scale if we wanted MPC in everything. If each use case had to bear the cost of developing and implementing a protocol, and if we had to constantly find relevant organizations willing to host the servers, it would not be widely adopted. The solution we came up with was Partisia Blockchain.
Let us look back three decades at how the internet was organized when I was a kid to illustrate why Partisia Blockchain is the way to go. Technologies like FTP, Gopher, Usenet, and Archie technically allowed everything the World Wide Web does today, but there was no dot-com boom. It took Tim Berners-Lee’s 1989 paper, “Information Management: A Proposal”. He rather modestly wanted to improve the way information was shared and managed among researchers at CERN and other institutions. He did not know he had just invented Amazon, eBay, Google, Yahoo, PayPal, Priceline… And of course he had not. He had invented an incredibly potential enabling technology. There might have been a short window where one boomer got the chance to ask “but what is WWW really useful for?” In fact, I know that guy. He was one of my professors the first year at my university. But it quickly turned out that the answer was “Everything!”
In my opinion, one of the most important developments happened in 1995, where the world saw the first version of the open source Apache web server. Now everyone could contribute to developing the WWW and everyone could almost by a single click install a web server and become an “Internet company”. After that no one looked back. There was no reason to ask what WWW was useful for. Everyone started to build what we have today, bottom up. By the early 2000s, Apache had become the dominant web server, powering over 70% of all websites. Apache was very much the enabler and the workhorse of the dot-com boom in the 1990s. Apache’s influence persists today, where 30% of all web servers still run Apache.
So, that was the question: How do we build the “Apache of MPC”? How do we make it possible for everyone to integrate MPC with a “single click”? Instead of having a few MPC companies pursue use cases, we needed to make the technology seamlessly available to everyone to kickstart the building of the MPC internet bottom up. The MPC equivalents of Amazon, eBay, Google, Yahoo, PayPal and Priceline would follow. You will build those! Of course, we needed programming languages and compilers to facilitate this. And we needed tools for integrating MPC with the existing internet technology. That is a lot of work, but it is not fundamentally different from building something like Apache. It is software. However, a major obstacle we were left contemplating was the problem of finding servers to run the protocols. This was an organizational problem, not a software problem. The solution we went for was a blockchain organizing staked and vetted organizations and individuals willing to run the MPCs. Servers hosted by blockchain participants can programmatically be scrambled when needed for an MPC: MPC-as-a-service. You can read more about the Partisia Blockchain architecture here [TBA]. Crucially this converted an organizational problem into a software one. And Partisia Blockchain was born.
There is still a lot of work to be done towards the ultimate dream of making MPC as efficient as computing on a single machine. This is one of the problems I focus on as a university researcher. However, in Partisia Blockchain we are now finally implementing a full-stack, single-click solution to integrate MPC into everything. You should join us in building the workhorse of the MPC internet and start integrating MPC into everything. The rest, I hope, will soon be internet history.
For me, blockchain and MPC represent an ongoing professional life journey. In the future I have two main means of transportation for the journey. From my role as a university researcher, I aim to continually develop better MPC protocols. Through Partisia Blockchain, I hope to help create “the Apache of MPC”. It has been a 21-year journey so far. We came a long way, but we also have a long road in front of us. Let us see where we are in 21 years from now. By 2045, I hope that if anyone asks, “But what is MPC really useful for?” the answer will be a bemused, “Everything!!!”, and that Partisia Blockchain is organizing 30% of the world’s MPC servers.
Until then, let’s get to work!
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
In April 2024, Partisia Blockchain achieved significant milestones, including forging partnerships with TPC Ventures and announcing our integration of the $MPC token on StakingRewards.com. We were also proud to announce our membership with the Swiss Blockchain Federation and our Ledger integration with the Partisia Blockchain app. Our presence at various events across the globe this month, such as the TEAMZ Web3 Summit and Token2049, showcased our commitment to innovation and collaboration. Let’s explore our ecosystem updates and key features in the press.
This month we announced our partnership with TPC Ventures, a player in the Web3 space, offering venture capital, development, and consulting services. Teaming up with Sensei Node, TPC Ventures brings a wealth of expertise to the table, providing professional validation and adoption services to bolster our network.
StakingRewards.com, a platform dedicated to collecting, ranking, and simplifying the staking process for various protocols, is now integrating the $MPC token. This integration aims to streamline the staking process and spotlight our unique rewarding structure. With over 200,000 monthly visitors, their platform offers a prime opportunity to reach a broader audience and showcase our rewarding model.
Additionally, Moonrig, a platform aspiring to become the leading rating agency in the digital currency industry, is striving to recruit credible research analysts to conduct deeper financial analysis of digital currencies. This endeavor promises to offer better insights to retail investors and contributes significantly to legitimizing the industry. This collaboration marks another significant step towards widespread adoption and recognition.
Now, you can seamlessly access the Partisia Blockchain app on Ledger devices, thanks to the successful completion of the Kudelski audit in March 2024. With Partisia Blockchain’s inclusion in the Ledger App catalog and support on Ledger hardware devices, MPC token holders can securely store, send, and stake their tokens. This collaboration brings together the cutting-edge security of Ledger, a leading hardware wallet provider, with the functionality of Partisia Blockchain, offering users unparalleled peace of mind and convenience. Get started with our easy-to-follow instructions here.
It is with great pride that we share our membership with the Swiss Blockchain Federation. This prestigious membership marks a significant step for Partisia Blockchain as we join forces with other industry leaders to solidify Switzerland’s position as a global blockchain hub. Together, we are committed to fostering a robust legal framework and innovation in the blockchain space.
The Partisia Blockchain team had an eventful week in Dubai, navigating through challenging weather conditions. At Token2049’s Restaking and Infra Day, Bruce Ahn, Head of Adoption, delivered two presentations. He introduced the BYOC blockchain and the programmable custody solution (MOCCA), emphasizing the significance of programmability and interoperability for Web3’s success. Bruce highlighted how these innovations are pivotal in shaping the future landscape of blockchain technology. At the TEAMZ Web3 Summit in Tokyo, our community engaged with the Partisia Blockchain team. Kurt Nielsen, Partisia Blockchain’s President, took center stage, shedding light on Real World Assets (RWA), blockchain adoption, and more in his keynote. Tokyo witnessed insightful discussions throughout the event, including an RWA panel hosted by EMURGO and engaging dialogues spanning various topics. In Estonia, Shirly Valge, Chief of Growth at Partisia Blockchain, recently took the stage at the Banana Conf (formerly NFT Tallinn) to delve deep into key blockchain topics. She led a panel discussion on the transformative power of blockchain in supply chain connectivity, exploring themes such as real-world asset tokenization, and shared invaluable insights on data privacy and artificial intelligence. Ibiza Tech Forum 2024 where the future of technology unfolds against the backdrop of the vibrant Balearic island, was also an event to remember in April 2024. Amidst the bustling atmosphere, global leaders and tech enthusiasts converged, including the Partisia Blockchain team. Shirly Valge took the stage to deliver a keynote on AI and the critical role of Privacy Enhancing Technology, while Maria Cocu, our Community Growth and Engagement Associate, immersed herself in discussions revolving around community expansion and engagement enhancement strategies. Balearic Islands served as the perfect setting for meaningful connections and cutting-edge insights into the tech landscape. Stay tuned for next month as Shirly Valge will be delivering a keynote and workshop at Block Split in Dalmatia during 27–30 May 2024.
Last April witnessed an uptick in publicity with Partisia Blockchain being mentioned in more than a thousand media outlets. A few highlights include Japanese Asahi TV’s news segment focusing on Web3’s growing importance in Japan and featuring our team members at the TEAMZ Web3 Summit in Tokyo. Our co-founder Brian Gallagher delved into the DeFi trends with Mario Nawfal on X Spaces broadcast. Elsewhere Cointelegraph ran a feature on Partisia Blockchain’s differentiators and solutions it offers and it published a piece on our Grants Program. In another television news segment, Denmark’s TV2 interviewed one of our co-founders Peter Frandsen. The Danish television reportage highlights the importance of data security, the Scandinavian country’s efforts in safeguarding against cyberthreats amid ongoing geopolitical volatility and the need for the data security infrastructure. Also in Denmark, the Aarhus University ran a video featurette about multiparty computation with commentary from Ivan Damgård and Peter Frandsen.
In April, we announced that wBTC will be added as a supported BYOC token on our platform. This integration is a significant step forward in enhancing interoperability within the Partisia Blockchain ecosystem. With wBTC support, users will enjoy seamless gas payments and expanded functionality, opening up new possibilities for decentralized finance and asset management.
Phase 1 of the zkCross Network is now live! zkCross, a zero-knowledge-based DEX, has been launched on Partisia Blockchain, paving the way for a seamless cross-chain collateralized DeFi protocol. This initial phase of the launch facilitates asset swapping and bridging into Partisia Blockchain’s BYOC network, with Phase 2 scheduled for early June. Phase 2 will see the rollout of a full-fledged native DEX on our network. For more details on this exciting announcement, read further here. Our AirDrop program is steadily progressing, with additional assets being bridged into the network. Throughout April, we witnessed a steady growth in Total Value Locked (TVL), accompanied by an increase in staked $MPC, bridged assets, and wallet counts. As we look ahead, we anticipate further growth catalyzed by the launch of zkCross and other dApps aimed at fostering increased activity within the chain.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Wrapping up a strong first quarter at Partisia Blockchain! This month was marked by significant milestones. First and foremost, our $MPC token is now listed on multiple exchanges, a major achievement for our ecosystem. Additionally, we are introducing staking rewards for $MPC holders and integrating with Ledger for enhanced security. We are privileged to announce the appointment of Dan Zaitsev as our Head of Marketing, underscoring our commitment to innovation. Reflecting on our presence at ETHDenver, we are proud of the impactful partnerships forged, demonstrating our dedication to collaboration. Stay tuned for more ecosystem developments and community initiatives as we continue to drive innovation in the blockchain industry.
March 2024 marked the pivotal moment we have all been waiting for. Partisia Blockchain proudly announced the listing of the $MPC token on multiple exchanges, including KuCoin, Bitfinex, Gate.io, Bitrue, and more soon to follow. Deposits and trading of Partisia Blockchain’s $MPC token on these platforms commenced on 19 March 2024, marking a monumental leap forward for our ecosystem. Renowned for our leadership in privacy-preserving, interoperable and sustainable blockchain solutions, this listing reaffirms our commitment to redefining security, trust, interoperability, and reliability within the blockchain industry.
To time the exchange launch, we also began to acquaint our new community with our unique technology and demonstrate how it compares with others in the industry. What is the $MPC Token, you may ask? Stay tuned for comparison charts highlighting its performance, privacy features, cross-chain messaging capabilities and custody solutions. Be on the lookout for more technology reviews of our unique blockchain, and please share and spread the word.
But that is not all. We are introducing staking rewards for $MPC token holders. Stake your $MPC tokens to unlock substantial incentives across various liquid assets, while also bootstrapping the network. Additionally, BYOC tokens (ETH, BNB, MATIC, USDC and USDT) are utilized for block production, further enhancing the network’s robustness. Dive into our tokenomics with Kurt Nielsen, where we delve into what makes us unique, our philosophy, and future plans for development. Learn about the high-level mechanics of the $MPC token, including staking benefits, by watching our informative video here. Ready to stake your claim in the future of blockchain? Follow our staking instructions here.
We were also excited to announce the integration of the Partisia Blockchain and Kudelski-audited MPC app with Ledger, a leading hardware wallet provider. This collaboration empowers MPC token holders with the ability to securely store, send and stake their MPC tokens using Ledger hardware devices. By joining forces with Ledger, we are providing our community with enhanced security and convenience, further solidifying our commitment to safeguarding their assets and expanding accessibility to our ecosystem.
We are delighted to share our collaboration with Google Cloud Partners, marking a significant milestone in our journey to revolutionize the blockchain landscape with MPC, blockchain and node network technologies. This partnership not only signifies our commitment to innovation, but also opens doors for seamless deployment on the Google Cloud Marketplace, facilitating accelerated mass adoption of our solutions. Together with Google Cloud Partners, we are poised to drive forward the accessibility and integration of our technologies, paving the way for a more interconnected and secure digital future.
Last month, Partisia Blockchain announced the appointment of Dan Zaitsev as the Head of Marketing. Dan brings a wealth of experience in tech innovations and marketing expertise to his role, further strengthening our commitment to innovation and excellence in the blockchain industry. With a remarkable background and a track record of successes, Dan’s arrival marks a pivotal moment for our team.
Taking us back to early March, ETHDenver marked a dynamic kickoff to spring, filled with days of insights, collaboration and networking. Let’s recap the exciting partnerships we announced during this event:
Our journey at ETHDenver was eventful. From fruitful meetings to new partnerships, we extend our gratitude to our community for joining us. Dive into the Denver Dailies for further details and see you next year.
Both stakers and node operators were once again rewarded with MPC tokens for staking. We gave out over 2.6 million $MPC tokens for the Q7 rewards. Alongside this, we also began to see higher on-chain transactions. This translated to the node operators earning more than 100,000 in BYOC tokens. As the network grows further, we anticipate further earnings by our node operators. Look for an opportunity for delegated stakers to earn these BYOC rewards in the future.
In the ecosystem, notable advancements have taken place in March. DelNorte launched its project in one of the municipalities in El Salvador, beginning the minting of official property deeds. Check out our Twitter spaces AMA session with Del Norte CEO Anton Glotser to learn more. Nova Miningverse is gaining momentum, boasting over 1400 unique transactions. Additionally, zkCross (formerly TeraBlock) is on the verge of launching their initial bridging platform, with subsequent work beginning to launch a swap/DEX. First month of spring witnessed a significant surge in dApps launching on mainnet, with more coming in April.
We extend our thanks to our community for their unwavering support and enthusiasm. Stay tuned for more exciting developments and initiatives in the coming months.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
ZUG, 26 MARCH 2024. The Partisia Blockchain Foundation, a pioneer in privacy-centric and interoperable blockchain solutions, is proud to announce the launch of its Grants Program. Aimed at fueling innovation within the blockchain ecosystem, this program is set to provide crucial financial support to projects that leverage the unique features of the Partisia Blockchain to address pressing challenges in privacy, interoperability, and scalability.
The Grants Program is open to entrepreneurs, developers, and innovators worldwide with projects that not only solve significant problems but also demonstrate a clear path to commercial viability and scalability. Successful applicants will receive funding in $MPC tokens, along with access to a vast network of industry experts and resources to bring their vision to reality.
Co-founder of the Partisia Blockchain, Brian Gallagher, remarked, “We are at a pivotal moment in the evolution of blockchain technology. The Partisia Blockchain Grants Program represents our commitment to supporting projects that share our vision of a more private, interoperable, and scalable blockchain ecosystem. We believe in empowering developers and entrepreneurs to build solutions that can truly make a difference in the world.”
Applications for the Grants Program are now open, with the foundation seeking proposals that exhibit a strong understanding of the Partisia Blockchain’s capabilities, a detailed financial and growth model, and a clear benefit to the broader blockchain community.
The Grants program is divided into two types:
For: Start-ups looking to build or enhance a business and major integrations
Application steps: https://partisia.link/grants
For: Teams looking to build smaller projects, proof of concepts, community tools or for small integration.
Application form: https://partisia.link/fast-track-grants-form
Applications for the Grants Program are now open, with the Foundation seeking proposals that exhibit a strong understanding of the Partisia Blockchain’s capabilities, a detailed financial and growth model, and a clear benefit to the broader blockchain community.
About Partisia Blockchain: The Partisia Blockchain is designed from the ground up to address the key challenges of privacy, interoperability, and scalability in the blockchain space. By combining cutting-edge cryptographic solutions with a novel consensus mechanism, Partisia Blockchain aims to set new standards in secure and efficient blockchain operations. Unlock your project’s potential with Partisia Blockchain’s 100 million $MPC Grants Program for ecosystem growth and mass token adoption.
Apply now: https://partisiablockchain.com/develop/grants-program/
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
ZUG, 25 MARCH 2024. Partisia Blockchain is pleased to announce the appointment of Danylo Zaitsev as the Head of Marketing, effective immediately. Danylo brings a wealth of experience in tech innovations and marketing expertise to his role, further strengthening our commitment to innovation and excellence in the blockchain industry.
With a background rooted in Ukraine, Danylo embarked on his tech journey 20 years ago as a product marketing manager. Over the past eight years, he has served as a C-level executive and founder, garnering invaluable experience in startups and tech enterprises. His track record of successes includes assisting numerous tech companies worldwide in building and scaling profitable businesses from inception.
In his current role at Partisia Blockchain, Danylo will work closely with the senior leadership team to enhance marketing strategies to further increase brand visibility and market penetration. His adeptness at navigating complex challenges positions him as a valuable asset in our goal of growth and market leadership.
Prior to joining Partisia Blockchain, Danylo held various leadership roles within the tech sector, building his skills in marketing, product development and business strategy. His dedication to excellence and passion for technology make him a natural fit for his role as Head of Marketing.
Partisia Blockchain is privileged to welcome Danylo Zaitsev to the team and anticipates his invaluable contributions to furthering the organizational objectives. His appointment underscores our commitment to assembling top-tier talent and reinforces our position as a leader in the blockchain industry.
About Partisia Blockchain: Partisia Blockchain brings unparalleled opportunities by empowering privacy-preserving, interoperable and sustainable innovation for fairness and transparency. It fuels the most secure and efficient networks to solve global problems. Distilled with 35 years of rigorous research, Partisia Blockchain future-proofs solutions, solves tomorrow’s challenges by powering fair, secure, distribution of benefits. While preserving privacy and confidentiality, it brings accountable, transparent and decentralized governance. Learn more: www.PartisiaBlockchain.com
Stay updated: Website • Twitter • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
Hello, Partisia Blockchain enthusiasts!
We are pleased to announce an exciting community contest to celebrate the first exchange listings of $MPC. It is not just a celebration; it is a challenge that comes with rewards.
The challenge awaits.
We are calling on the traders, the streamers, the blockchain believers, and especially the early adopters who have been with us on this journey. The first three participants to post a live stream of themselves trading $MPC on any exchange will win a prize in $MPC tokens. Whether you are a seasoned trader or just starting out, this is your moment to shine and potentially earn some $MPC for your portfolio.
There are two ways you can participate.
Screenshot contest:
First 10 participants to post a valid screenshot of a trade will earn 100 $MPC each. Valid for each exchange that lists us within a one week period. Multiple entries per participant accepted.
Streaming to Parti.com:
Valid for each Exchange that lists us within a one week period. Multiple entries per participant accepted. The winners will be announced a week after the streaming ends.
Streaming to other platforms:
Valid for each Exchange that lists us within a one week period. Multiple entries per participant accepted. The winners will be announced a week after the streaming ends.
This contest is not just about winning prizes; it is a celebration of our community’s growth and the milestones we have achieved together. By participating, you are not just showcasing your trading prowess; you are also supporting the broader vision of Partisia Blockchain. It is a unique opportunity to be part of something bigger, to engage with like-minded individuals, and to help shape the future of decentralized trading and blockchain technology.
Ready, set, go!
We cannot wait to see your screenshots and live streams and share in the excitement of the first exchange listing of $MPC. Remember, it is not just about trading; it is about being part of a community that is pushing the boundaries of blockchain technology. Let’s make this contest a moment to remember.
Good luck to all participants. May the fastest traders win!
Happy trading,
Partisia Blockchain Community Team
From forging strategic partnerships at ETHDenver to launching our highly anticipated 25 million $MPC AirDrop program, the shortest month of the year has been a whirlwind of excitement and growth for Partisia Blockchain. We solidified ties with Georgia’s Innovation and Technology Agency, ventured into new realms with TeraBlock and Verida through engaging AMAs, celebrated the ingenuity of our hackathon winners, and embarked on a mission to empower Rust developers with TinTinLand. With fast track grants, educational initiatives, and a thriving community, we are ready for even greater success ahead. Thanks to our incredible community for your unwavering support – let’s make Q1 unforgettable!
In early February 2024, Partisia Blockchain achieved a significant milestone in advancing innovation by solidifying ties with Georgia’s Innovation and Technology Agency (GITA) under the Ministry of Economy and Sustainable Development. Partisia Blockchain will play a key role in shaping the minds of participants in GITA’s educational programs, contributing insights on MPC, homomorphic encryption and their integration with blockchain technology. This commitment to education reflects the shared vision of advancing technology while ensuring knowledge and understanding pave the way for a sustainable future.
ETHDenver was a platform for new partnerships, expanding our horizons and widening the reach of our unique technology. Trustswap, a provider of decentralized finance tools for token holders and Web3 businesses, is integrating Partisia Blockchain into their Crypto App, expanding MPC accessibility to 5 million users. Partisia Blockchain also partnered with Sierra Block Games, Web3 development, consulting and educational services organization, for validator services and adoption support. We will also collaborate with IoTex to realize the Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN), safeguarding users’ IoT data ownership and monetization while rewarding data use without exposing confidential details. Together, they aim to protect users’ private IoT data and enable its secure utilization.
We were thrilled to launch our first official AirDrop on 1 February, marking a significant milestone for ecosystem adoption. With the governance vote for MPC token transferability looming, this AirDrop underscored Partisia Blockchain’s vision. Boasting an impressive pool of 25 million $MPC tokens, it offered unparalleled opportunities for early adopters. The first tranche kick started ecosystem expansion. Participants gained firsthand experience with leading MPC and blockchain technology, secured the network, and explored innovative dApps. As we geared up for MPC token listing, this AirDrop invigorated the ecosystem.
We were thrilled to see our AirDrop program resonate strongly with the community, especially given the impressive growth in our ecosystem. Since its inception, our ecosystem has witnessed remarkable progress:
These statistics underscore the growing momentum and enthusiasm within our community, and we have you to thank. Detailed participation information can be found on our official AirDrop page.
We launched our fast track grants in February 2024. These grants are geared toward developers planning to build something smaller in nature, and does not have to be geared toward building a business. We will pursue developers who wish to contribute to the community by building examples, PoC, and tools. For more information about our Grants Program, click here.
On 14 February, we held the second AMA with the up and coming cross-chain decentralized exchange TeraBlock. This time around we invited TeraBlock’s Shivam Tandon, Founder and CEO, and Muhammad Ali, Chief Commercial Officer, to provide insights from a non-developer’s perspective, on why Terablock is a game changer for DeFi, powered by the Partisia Blockchain. On 22 February, we held a dual AMA with ecosystem partner Verida. Mathias Glintborg, our Head of Product, and Chris Were, CEO of Verida, both introduced the projects to each other’s community, its use cases and technological achievements. An excellent primer for both data on decentralized Identity for Web3 (Verida) as well as multiparty computation.
Our Building Privacy in Web3 Hackathon concluded with a bang. We announced six winners, all projects that showcase our unique capabilities. From random number generations to supply chain management to zero-knowledge games, developers came out to really showcase their talent and show us how our amazing technology can be used. We will be continuing to work with them to bring them into the mainstream.
Partisia Blockchain and TinTinLand are set to launch a learning program aimed at attracting more Rust developers to our ecosystem. Currently, only 22,000 out of 30 million global developers are engaged in Web3. The collaboration aims to scale the developer ecosystem and unlock the Chinese developer community, attract new Rust developers from China, organize hackathons, workshops, and developer meetups, and promote our Grants Program. Together, we hope to expand developer engagement and foster growth within our ecosystem, particularly in China.
Thanks again to our amazing community for your dedicated support, we look forward to an exciting end to Q1 next month.
Stay updated:
Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube

Last week, the Partisia Blockchain team journeyed to Georgia, a land rich in cultural heritage as the birthplace of wine and now at the forefront of blockchain innovation. Here is a short recap of our fruitful trip.
Last Thursday marked a milestone as Partisia Blockchain formalized its collaboration with the Georgian Innovation and Technology Agency (GITA) through the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU). This pivotal agreement with GITA under the Ministry of Economy and Sustainable Development sets the stage for collaborative efforts aimed at driving advancements in Web3 technology, both within Georgia and the wider Caucasus. By leveraging their combined expertise and resources, Partisia Blockchain and GITA will explore innovative solutions and applications of blockchain technology, fostering joint support for innovative projects, educational initiatives and frameworks for implementation. This collaboration signifies a commitment to shaping the digital transformation landscape, contributing to economic growth, innovation and societal development in Georgia and beyond.

Our team had the pleasure of meeting with members of the Georgian Web 3.0 community, where we showcased the transformative potential of Partisia Blockchain and multiparty computation (MPC) technology, our latest MOCCA solution and a range of other advantages of MPC. Additionally, we introduced our Grants Program aimed at fostering innovation in the Caucasus. In Tbilisi, we were treated to an exclusive demo of the Nova Miningverse video game, a tangible showcase of Partisia Blockchain’s capabilities. This was followed by an informal meeting with the team behind the game.
Last Friday began with a meeting with Razhden Kuprashvili, Head of the Georgian Anti-Corruption Bureau and his team at the Administration of the Government of Georgia. We discussed the potential of MPC and blockchain technology in combating corruption. Later, we exchanged ideas with entrepreneur Vako Turnava at the offices of his companies Sweeft and Skillwill. Conversations revolved around the various applications of MPC and privacy-enhancing technologies, emphasizing the importance of education and training.
This trip showcased the possibilities of blockchain technology and strengthened our commitment to driving positive change in Georgia and beyond. Stay tuned for updates as we continue to push the boundaries of innovation and collaboration in the world of Web 3.0.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
January marked a strong start to 2024 for Partisia Blockchain, featuring groundbreaking developments and strategic partnerships that define our dynamic journey for the year. Unveiling the revolutionary MPC On-Chain Custody Advanced (MOCCA) solution in Davos, we explored the transformative potential of MPC and delved into its pivotal role in reshaping the digital landscape. Engaging in impactful discussions during the World Economic Forum, we highlighted the importance of blockchain in rebuilding trust and announced collaborations with five innovative projects. Interviews with our thought leaders shed light on the evolving digital terrain, covering artificial intelligence discussions in Davos and the potential of Web3 and MPC. As we venture into February, exciting initiatives include the AirDrop program and a thriving Hackathon, accompanied by significant tech highlights, promising a month of continued innovation.
Partisia Blockchain introduced a revolutionary leap in decentralized custody solutions with the unveiling of MOCCA (MPC On-Chain Custody Advanced solution) in Davos during the World Economic Forum. MOCCA stands out for its decentralized and programmable multichain custody, offering enhanced security, compliance, and privacy. Backed by 35 years of MPC research, MOCCA addresses limitations of traditional smart contracts and centralization, providing institutions and organizations with genuine decentralization and flexibility in securing digital assets across multiple chains. Notable features include fully programmable custody smart contracts, blockchain-agnostic multichain functionality, and swift, cost-effective deployment directly on-chain.
Davos 2024 marked a week of unparalleled influence and innovation for Partisia Blockchain, solidifying its presence on Promenade during the World Economic Forum (WEF) for the second consecutive year. The launch of the MOCCA solution set a new industry standard, addressing infrastructure fortification, transparency, and expanded usability. Discussions in Davos focused on the pivotal role of blockchain in rebuilding trust, with an increased emphasis on regulatory landscapes, particularly Europe’s MiCA regulation and global supervisory actions. Brian Gallagher, Co-Founder of Partisia Blockchain, emphasized the importance of building decentralized trust networks, and discussions spanned cross-chain liquidity, Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), stablecoins, cybersecurity priorities, and identity management. We were proud to have Shirly Valge, Chief of Growth, participate in the first-ever Women in Web3 Global Summit, connecting with visionary women leaders. Beyond more than 40 engagements, fruitful meetings resulted in letters of intent, collaborations, and agreements, making Davos 2024 a landmark event shaping the future of blockchain through regulatory advancements and technological breakthroughs, highlighting the industry’s commitment to innovation and trust-building.
Kurt Nielsen explored the transformative potential of multiparty computation (MPC) for 2024 in a recent blog. Partisia Blockchain envisions MPC becoming fundamental for secure, collaborative digital interactions. Key highlights include mainstream integration across industries, with a focus on finance and healthcare for safeguarding sensitive data. MPC will revolutionize decentralized identity, enhance privacy in blockchain, offer quantum-ready solutions, and accelerate innovation in artificial intelligence and machine learning. Financial sectors and healthcare research will lead MPC adoption, while DeFi expands beyond blockchain, addressing edge computing security and driving standardization initiatives.
In recent press interviews, Partisia Blockchain’s thought leaders shared valuable insights into the rapidly evolving digital landscape. Shirly Valge engaged in an insightful conversation with CoinDesk in Davos, delving into discussions where AI took center stage. As our Chief of Growth, she provided a unique perspective on the dynamic landscape. Brian Gallagher, Co-Founder of Partisia Blockchain, explored the potential of Web3 and secure multiparty computation (MPC) in an interview with the Human and Machine Channel. The discussion centered around how MPC ensures data privacy in the ever-evolving digital realm.
This year’s first month has been a flurry of activities with new partnerships. And Davos was a perfect platform for partnerships. During the World Economic Forum, we announced new projects partnering with Partisia Blockchain.
February marks the launch of the Partisia Blockchain AirDrop program. With the upcoming governance vote for the MPC token transferability just around the corner, this is a testament for the Partisia Blockchain’s vision. The program features an impressive pool size of 25 million MPC tokens. The program offers an unparalleled opportunity for the early adopters of the Partisia Blockchain. The first tranche of the 25 million MPC token AirDrop program commencing on 1 February 2024 will kickstart the further expansion of our ecosystem. Our Hackathon is moving along well with close to one thousand participants. The end of the Hackathon is set for 13 February 2024, and judging to conclude by March. We are anticipating to see some great projects come out of it. And do not miss the Crypto Stalkers AMA this month. Tiago Serôdio is going to introduce the Crypto Stalkers community to Partisia Blockchain and will answer their questions.
The node operators voted in favor of onboarding USDT as a BYOC token. This now adds another stable token as a form of payment to the Partisia Blockchain network. Another proposal to expand the BYOC portfolio will be put forward this month. The node operators will be asked to vote for the inclusion of the wBTC token into the BYOC portfolio. Finally, the Partisia Blockchain team will be attending ETH Denver from 23 February until 3 March. The delegation will consist of key persons and look forward to meeting you in Colorado.
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube
For the second consecutive year, Partisia Blockchain took center stage in Davos during the World Economic Forum (WEF), marking a milestone with the largest delegation to date. Despite the cold weather, tight security and a packed agenda, our mission to promote Partisia Blockchain remained unwavering, leading to more than 45 engagements—spanning keynote addresses, panel discussions, industry sessions and speeches over five dynamic days.
A defining moment occurred in Davos with the launch of our MPC On-Chain Custody Advanced (MOCCA) solution. This decentralized, programmable, multichain custody solution set a new industry standard, addressing the pressing need for fortified infrastructure, transparency and expanded usability.
The WEF’s overarching theme, “Rebuilding trust”, framed numerous discussions on blockchain’s pivotal role in restoring trust. Our engagements with decision-makers consistently highlighted blockchain and other innovative technologies as essential tools in the pursuit of regaining trust.
Davos 2024 witnessed an increased focus on the regulatory landscape within the blockchain sphere. Discussions delved into Europe’s MiCA regulation and actions by global supervisory bodies. The consensus underscored the vital role of key infrastructure, exemplified by Partisia Blockchain, in strengthening security, privacy and transparency. This regulatory exploration unfolded amidst a surge of interest in decentralized finance (DeFi) and tokenization.
In DeFi, stakeholders explored its potential to rebuild trust through enhanced reliability. Conversations spanned liquidity, risk management and the disruptive impact on traditional finance, with trustless technology emerging as a viable solution. Tokenization, powered by blockchains like ours, took center stage, showcasing its transformative capacity to simplify securities issuance and provide irrefutable ownership through immutable records.
Trust, a pervasive theme in Davos, seamlessly aligned with Partisia Blockchain’s mission. Insights from Brian Gallagher, our Co-Founder, emphasized the importance of building decentralized trust networks. The regulatory imperative for managing risk across digital asset markets highlighted the collective responsibility required for a resilient and inclusive market environment. Technology’s role in enhancing transparency and mitigating risks showcased blockchain’s potential.
Brian Gallagher emphasized cross-chain liquidity’s necessity, pointing to the vital role of multichain solutions. Discussions on Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and stablecoins explored their harmonious coexistence, delving into regulatory nuances, stability and trust. The week culminated with a focus on cybersecurity priorities, positioning blockchain’s collective responsibility as pivotal for a secure digital future.
Identity management as part of trust building was a key conversation in Davos. Shirly Valge, our Chief of Growth, participated in a panel on Web3 and digital identity, highlighting user data control and fraud prevention. The recurring theme of infrastructure underscored blockchain’s foundational role in shaping the evolving Web3 landscape. Security, a constant thread, scrutinized Bitcoin mining, digital identity and the Web3 venture landscape, emphasizing the need for technology to balance scalability, usability, interoperability and digital security.
Beyond engagements, the Partisia Blockchain delegation held fruitful meetings with potential partners, resulting in letters of intent, collaborations and agreements.
In retrospect, Davos 2024 stands as a landmark event, revealing transformative themes that will undoubtedly shape the future of blockchain. From regulatory advancements to technological breakthroughs, the week served as a testament to the industry’s commitment to innovation and trust-building.
Read our daily wraps here: 15 January 2024, 16 January 2024, 17 January 2024, 18 January 2024, 19 January 2024
Stay updated: Website • X • Discord • Telegram • LinkedIn • Facebook • Instagram • GitLab • Medium • YouTube