The emergence of Web3 and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has ushered in a new era of digital innovation, promising a paradigm shift towards greater transparency, efficiency and accessibility. However, the realization of this necessitates addressing several technical and conceptual challenges inherent in the underlying blockchain technology.
The “blockchain trilemma”, a well-documented conundrum, highlights the intricate trade-offs between decentralization, security and scalability. Achieving an optimal balance between these three pillars is essential for creating a robust, secure and efficient decentralized ecosystem capable of supporting widespread adoption.
This confluence of challenges necessitates the development of sophisticated solutions that can simultaneously address the blockchain trilemma while ensuring robust privacy protection. Partisia Blockchain emerges as a sophisticated response to these challenges through the integration of advanced privacy-preserving cryptographic techniques with a high-performance blockchain architecture.
Partisia Blockchain is a Layer 1 blockchain that redefines the paradigm of decentralized technology by seamlessly integrating privacy-preserving mechanisms with a high-performance architecture. This unique approach addresses the inherent challenges faced by traditional blockchain models, such as scalability limitations and the potential compromise of sensitive data due to the public nature of distributed ledgers.
Central to Partisia Blockchain’s innovation is the implementation of a privacy layer that enables zero-knowledge (ZK) computations to run in parallel with activities on the public blockchain. This groundbreaking integration of blockchain technology and multiparty computation (MPC) vastly expands the possibilities of decentralized applications, allowing for confidential transactions, secure data sharing, and regulatory-compliant solutions.
The platform’s consensus algorithm FastTrack model, a novel approach that combines optimistic block production with a robust Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) mechanism, ensures both rapid transaction validation and the highest levels of security.
Addressing the scalability challenge, Partisia Blockchain employs a comprehensive true sharding solution. This approach dynamically expands the network with manageable segments (blockchains), allowing for efficient processing of high transaction volumes without compromising consensus or security.
To foster a more interconnected blockchain ecosystem, the network has implemented a native collateral bridge, facilitating the secure transfer of assets and information between the Partisia Blockchain and other networks, promoting interoperability and collaboration.
The commitment to privacy extends to the MPC-as-a-Service platform, providing developers with a comprehensive suite of tools. This platform streamlines the orchestration of privacy-preserving computations, enabling a wide range of use cases, from confidential financial transactions to private auctions and secure data sharing.
Finally, Partisia Blockchain fosters a thriving and reliable network through a market for trust that incentivizes node operators to validate transactions, propagate information and provide MPC-as-a-Service. This mechanism ensures that the network is supported by transparent and efficient nodes; thereby, maintaining the highest standards of security and performance.
In this three-part series, we will dive deeper into performance, zero-knowledge technology, and the cross-chain messaging technology stack of Partisia Blockchain versus other solutions in the field.
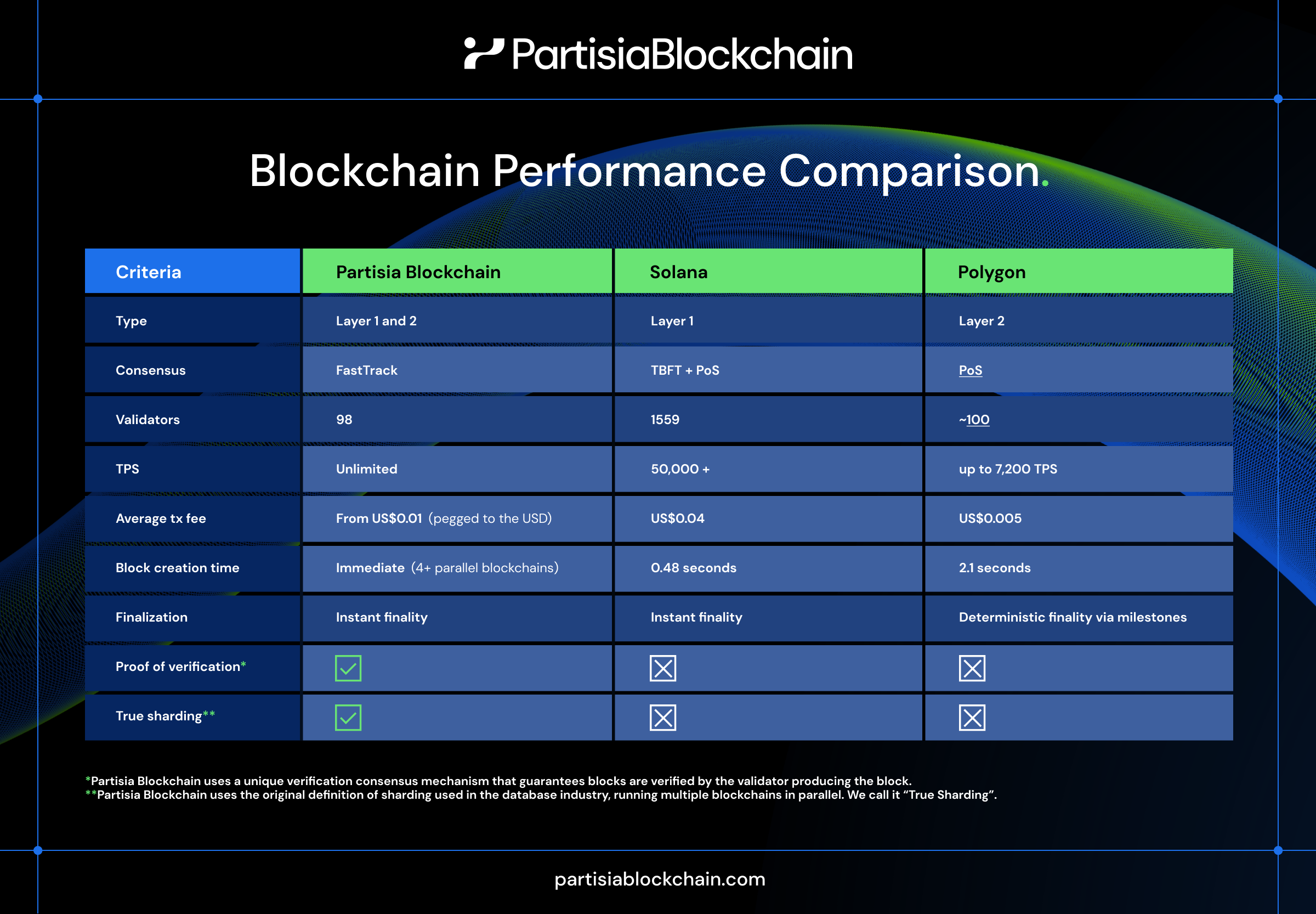
*Partisia Blockchain uses a unique verification consensus mechanism that guarantees blocks are verified by the validator producing the block.
**Partisia Blockchain uses the original definition of sharding used in the database industry, running multiple blockchains in parallel. We call it “True Sharding”.
Partisia Blockchain stands as a robust and adaptable Layer 1 blockchain that prioritizes privacy, scalability and decentralization. Its innovative FastTrack consensus mechanism, incorporating Proof of Justification (PoJ) and Proof of Finalization (PoF), ensures robust security and transaction finality. The Proof-of-Verification (PoV) mechanism further enhances security by guaranteeing that validators personally verified each block.
The scalability challenge is tackled through a dynamic sharding approach. Unlike traditional blockchain sharding, in Partisia Blockchain shards are an independent blockchain that can separately create, verify and validate a block. While most blockchains create one block at a time, Partisia Blockchain leverages its sharded architecture, now it is four shards (four chains), to generate four blocks at a time and there is no limit.
This architecture allows for true parallel blockchain processing. In the event of congestion, the system can dynamically create new shards, adding capacity on the fly. This dynamic scalability architecture theoretically enables the network to scale horizontally infinitely.
The platform’s versatility is further amplified by its support for diverse node types, each with specialized functions. These include reader nodes for accessing information, baker nodes for producing and validating blocks, ZK nodes for zero-knowledge computations and oracle nodes for oracle services. This diversity caters to a wide array of use cases, making Partisia Blockchain adaptable to evolving demands.
It is also important to mention that Partisia Blockchain eliminates the volatility and unpredictability often associated with blockchain transaction fees. This differs from traditional blockchain models with an approach that combines a fixed-fee structure tied to the US dollar, offering users stability and convenience. This means users know exactly how much they will pay for a transaction, making cost estimation straightforward and budgeting easier.
Furthermore, Partisia Blockchain offers flexibility in fee payments by not limiting them to the native $MPC token. Users can choose to pay network fees using other supported tokens, enhancing convenience and accessibility.
This feature we will explore further in this article.
Solana achieves high speed and scalability through its Proof of History (PoH) timekeeping mechanism, combined with Proof of Stake (PoS) and Tower BFT for consensus. Its Sealevel parallel smart contract execution and Turbine block propagation further enhance its performance.
Solana’s software is designed to get out of the way and let the hardware operate at capacity, while most blockchain systems need to work on optimizing the software to improve their throughput. As such, Solana scales naturally with bandwidth, SSDs, and GPU cores. It is a good solution, but resource-intensive and expensive for node operators.
The fee structure consists of a base fee per transaction and priority fee that allows users to expedite transactions by paying more during high network congestion. This fee is calculated dynamically, based on current demand and desired confirmation time. Solana also has a “rent” fee, a withheld balance in each account to cover on-chain data storage costs.
Polygon distinguishes itself by offering a multi-layered approach to scaling Ethereum. Its PoS sidechain provides a parallel network for faster and cheaper transactions while still maintaining compatibility with Ethereum. The Polygon zkEVM leverages zero-knowledge rollups to bundle and verify transactions off-chain, further increasing scalability and reducing costs.
With the Polygon 2.0 (zkEVM validium) update, the network is set to become a network of ZK rollup chains, enabling interoperability and a wider range of applications while maintaining the security of the Ethereum mainnet.
While offering significant scalability advantages over Ethereum, Polygon has challenges with transaction finality due to its reliance on checkpoints on the Ethereum mainchain. In its PoS chain, transaction finality is not immediate. It requires a waiting period before the transaction is considered final after a checkpoint sent to Ethereum. This process is slow and introduces the risk of deep chain reorganizations, affecting the overall user experience.
To address this, Polygon implemented the “Deterministic Finality via Milestones”. Milestones, similar to Ethereum’s checkpoints, signal the finality of blocks in the validator layer allowing to achieve faster finality, minimizing the risk of following an incorrect chain for an extended period. While the milestones solution addresses the finality issue, Polygon’s PoS inherently comes with certain limitations regarding throughput. The number of validators in the network is limited, which can potentially bottleneck the transaction processing capacity. Moreover, while zkRollups offer scalability advantages, they also have their own throughput limitations due to the computational requirements of generating zero-knowledge proofs.
Speaking about fees, Polygon offers lower transaction fees than Ethereum. The fees on Polygon PoS, consist of a base fee and a priority fee to speed up processing, both paid in $MATIC. The base fee, which fluctuates depending on network congestion, is then burned. Polygon zkEVM, based on zero-knowledge rollups, also incurs gas fees paid in $MATIC to cover computational costs.
Stay tuned for Part 2 of the series where we will delve deeper into the zero-knowledge technologies and compare Partisia Blockchain with other blockchains.